Page 101 - Libro 2
P. 101
6 — Ultrasound Following Surgery and Intervention
81
away from the side being examined. Occasionally, if the patient cannot lie supine, the examination can be performed with the patient in a sitting position. Conducting an examination with the patient sitting upright is not ideal because, in this position, the pa- tient often does not remain still and it adds strain to the sonographer.
Scanning Techniques
A standard carotid duplex ultrasound examination is performed for the CEA patient. The CCA, ICA, and ECA are examined using B-mode and color-flow imag- ing techniques. Spectral Doppler is taken throughout the vessels at the typical levels specified in Chapter 4. There are particular areas to be closely examined, and these are described in the following section.
Technical Considerations
Primary concerns for the evaluation of the CEA pa- tient include stenosis from residual plaque or intimal flap, suture narrowing, or thrombotic narrowing/ occlusion. The ultrasound findings along the endar- terectomy site as well as at the ends of the endar- terectomy site must be carefully examined for any of these primary concerns. In the immediate post- operative period, the information obtainable may be restricted to knowing whether there is flow in the distal cervical ICA. The quality of flow then also be- comes important to determine whether poststenotic turbulence exists.
The sonographer will, in all likelihood, not have any information on how the CEA was performed. It would be best to assume that a traditional CEA was performed and a patch was used. If a patch is identi- fied, it should be determined whether the patch is synthetic or autogenous. A synthetic patch may ap- pear to have a woven appearance to the walls (in the
case of a Dacron patch) or demonstrate two brightly echogenic lines (in the case of a PTFE, which is dou- ble layered). Vein patches will more closely resemble the native vessel.
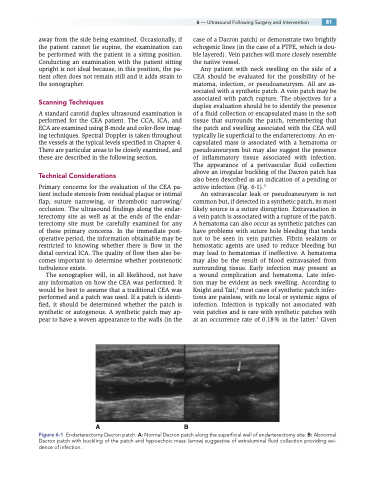
Any patient with neck swelling on the side of a CEA should be evaluated for the possibility of he- matoma, infection, or pseudoaneurysm. All are as- sociated with a synthetic patch. A vein patch may be associated with patch rupture. The objectives for a duplex evaluation should be to identify the presence of a fluid collection or encapsulated mass in the soft tissue that surrounds the patch, remembering that the patch and swelling associated with the CEA will typically lie superficial to the endarterectomy. An en- capsulated mass is associated with a hematoma or pseudoaneurysm but may also suggest the presence of inflammatory tissue associated with infection. The appearance of a perivascular fluid collection above an irregular buckling of the Dacron patch has also been described as an indication of a pending or active infection (Fig. 6-1).3
An extravascular leak or pseudoaneurysm is not common but, if detected in a synthetic patch, its most likely source is a suture disruption. Extravasation in a vein patch is associated with a rupture of the patch. A hematoma can also occur as synthetic patches can have problems with suture hole bleeding that tends not to be seen in vein patches. Fibrin sealants or hemostatic agents are used to reduce bleeding but may lead to hematomas if ineffective. A hematoma may also be the result of blood extravasated from surrounding tissue. Early infection may present as a wound complication and hematoma. Late infec- tion may be evident as neck swelling. According to Knight and Tait,3 most cases of synthetic patch infec- tions are painless, with no local or systemic signs of infection. Infection is typically not associated with vein patches and is rare with synthetic patches with at an occurrence rate of 0.18% in the latter.1 Given
AB
Figure 6-1 Endarterectomy Dacron patch. A: Normal Dacron patch along the superficial wall of endarterectomy site. B: Abnormal Dacron patch with buckling of the patch and hypoechoic mass (arrow) suggestive of extraluminal fluid collection providing evi- dence of infection.