Page 129 - Libro 2
P. 129
7 — Intracranial Cerebrovascular Examination
109
from the TICA, and coursing posteriorly, which can be seen with color Doppler. A fetal origin PCA can have a significant clinical impact on patients with ICA stenosis and/or vertebrobasilar disease and should be noted in the comments and on the interpretation.
Foramen Magnum Approach
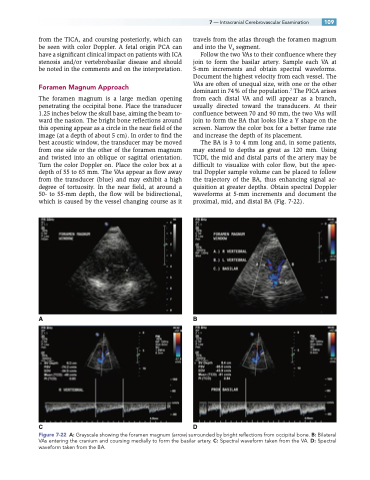
The foramen magnum is a large median opening penetrating the occipital bone. Place the transducer 1.25 inches below the skull base, aiming the beam to- ward the nasion. The bright bone reflections around this opening appear as a circle in the near field of the image (at a depth of about 5 cm). In order to find the best acoustic window, the transducer may be moved from one side or the other of the foramen magnum and twisted into an oblique or sagittal orientation. Turn the color Doppler on. Place the color box at a depth of 55 to 65 mm. The VAs appear as flow away from the transducer (blue) and may exhibit a high degree of tortuosity. In the near field, at around a 50- to 55-mm depth, the flow will be bidirectional, which is caused by the vessel changing course as it
travels from the atlas through the foramen magnum and into the V4 segment.
Follow the two VAs to their confluence where they join to form the basilar artery. Sample each VA at 5-mm increments and obtain spectral waveforms. Document the highest velocity from each vessel. The VAs are often of unequal size, with one or the other dominant in 74% of the population.7 The PICA arises from each distal VA and will appear as a branch, usually directed toward the transducers. At their confluence between 70 and 90 mm, the two VAs will join to form the BA that looks like a Y shape on the screen. Narrow the color box for a better frame rate and increase the depth of its placement.
The BA is 3 to 4 mm long and, in some patients, may extend to depths as great as 120 mm. Using TCDI, the mid and distal parts of the artery may be difficult to visualize with color flow, but the spec- tral Doppler sample volume can be placed to follow the trajectory of the BA, thus enhancing signal ac- quisition at greater depths. Obtain spectral Doppler waveforms at 5-mm increments and document the proximal, mid, and distal BA (Fig. 7-22).
AB
CD
Figure 7-22 A: Grayscale showing the foramen magnum (arrow) surrounded by bright reflections from occipital bone. B: Bilateral VAs entering the cranium and coursing medially to form the basilar artery. C: Spectral waveform taken from the VA. D: Spectral waveform taken from the BA.