Page 137 - Libro 2
P. 137
7 — Intracranial Cerebrovascular Examination
117
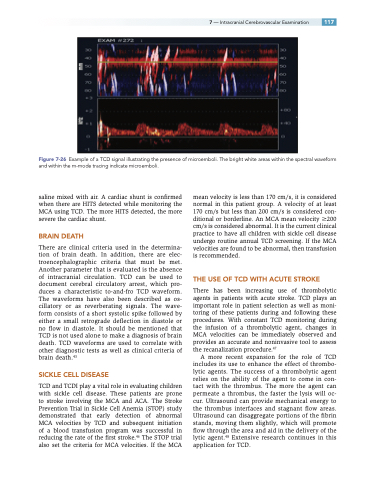
Figure 7-26 Example of a TCD signal illustrating the presence of microemboli. The bright white areas within the spectral waveform and within the m-mode tracing indicate microemboli.
saline mixed with air. A cardiac shunt is confirmed when there are HITS detected while monitoring the MCA using TCD. The more HITS detected, the more severe the cardiac shunt.
BRAIN DEATH
There are clinical criteria used in the determina- tion of brain death. In addition, there are elec- troencephalographic criteria that must be met. Another parameter that is evaluated is the absence of intracranial circulation. TCD can be used to document cerebral circulatory arrest, which pro- duces a characteristic to-and-fro TCD waveform. The waveforms have also been described as os- cillatory or as reverberating signals. The wave- form consists of a short systolic spike followed by either a small retrograde deflection in diastole or no flow in diastole. It should be mentioned that TCD is not used alone to make a diagnosis of brain death. TCD waveforms are used to correlate with other diagnostic tests as well as clinical criteria of brain death.45
SICKLE CELL DISEASE
TCD and TCDI play a vital role in evaluating children with sickle cell disease. These patients are prone to stroke involving the MCA and ACA. The Stroke Prevention Trial in Sickle Cell Anemia (STOP) study demonstrated that early detection of abnormal MCA velocities by TCD and subsequent initiation of a blood transfusion program was successful in reducing the rate of the first stroke.46 The STOP trial also set the criteria for MCA velocities. If the MCA
mean velocity is less than 170 cm/s, it is considered normal in this patient group. A velocity of at least 170 cm/s but less than 200 cm/s is considered con- ditional or borderline. An MCA mean velocity 200 cm/s is considered abnormal. It is the current clinical practice to have all children with sickle cell disease undergo routine annual TCD screening. If the MCA velocities are found to be abnormal, then transfusion is recommended.
THE USE OF TCD WITH ACUTE STROKE
There has been increasing use of thrombolytic agents in patients with acute stroke. TCD plays an important role in patient selection as well as moni- toring of these patients during and following these procedures. With constant TCD monitoring during the infusion of a thrombolytic agent, changes in MCA velocities can be immediately observed and provides an accurate and noninvasive tool to assess the recanalization procedure.47
A more recent expansion for the role of TCD includes its use to enhance the effect of thrombo- lytic agents. The success of a thrombolytic agent relies on the ability of the agent to come in con- tact with the thrombus. The more the agent can permeate a thrombus, the faster the lysis will oc- cur. Ultrasound can provide mechanical energy to the thrombus interfaces and stagnant flow areas. Ultrasound can disaggregate portions of the fibrin stands, moving them slightly, which will promote flow through the area and aid in the delivery of the lytic agent.48 Extensive research continues in this application for TCD.