Page 308 - Libro 2
P. 308
288
PART 5 — ABDOMINAL
PATHOLOGY BOX 18-1
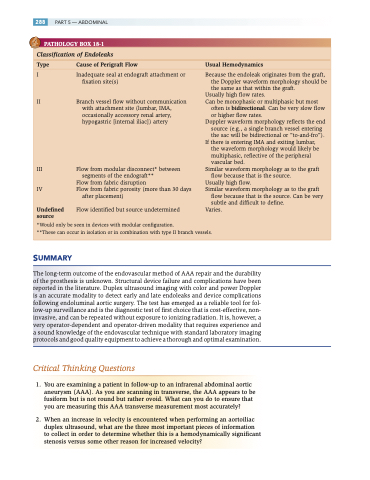
Classification of Endoleaks
Type Cause of Perigraft Flow Usual Hemodynamics
I Inadequate seal at endograft attachment or fixation site(s)
II Branch vessel flow without communication with attachment site (lumbar, IMA, occasionally accessory renal artery,
hypogastric [internal iliac]) artery
III Flow from modular disconnect* between segments of the endograft**
Flow from fabric disruption
IV Flow from fabric porosity (more than 30 days
after placement)
Undefined Flow identified but source undetermined
source
Because the endoleak originates from the graft, the Doppler waveform morphology should be the same as that within the graft.
Usually high flow rates.
Can be monophasic or multiphasic but most
often is bidirectional. Can be very slow flow
or higher flow rates.
Doppler waveform morphology reflects the end
source (e.g., a single branch vessel entering
the sac will be bidirectional or “to-and-fro”). If there is entering IMA and exiting lumbar,
the waveform morphology would likely be multiphasic, reflective of the peripheral vascular bed.
Similar waveform morphology as to the graft flow because that is the source.
Usually high flow.
Similar waveform morphology as to the graft
flow because that is the source. Can be very
subtle and difficult to define. Varies.
*Would only be seen in devices with modular configuration.
**These can occur in isolation or in combination with type II branch vessels.
SUMMARY
The long-term outcome of the endovascular method of AAA repair and the durability of the prosthesis is unknown. Structural device failure and complications have been reported in the literature. Duplex ultrasound imaging with color and power Doppler is an accurate modality to detect early and late endoleaks and device complications following endoluminal aortic surgery. The test has emerged as a reliable tool for fol- low-up surveillance and is the diagnostic test of first choice that is cost-effective, non- invasive, and can be repeated without exposure to ionizing radiation. It is, however, a very operator-dependent and operator-driven modality that requires experience and a sound knowledge of the endovascular technique with standard laboratory imaging protocols and good quality equipment to achieve a thorough and optimal examination.
Critical Thinking Questions
1. You are examining a patient in follow-up to an infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). As you are scanning in transverse, the AAA appears to be fusiform but is not round but rather ovoid. What can you do to ensure that you are measuring this AAA transverse measurement most accurately?
2. When an increase in velocity is encountered when performing an aortoiliac duplex ultrasound, what are the three most important pieces of information to collect in order to determine whether this is a hemodynamically significant stenosis versus some other reason for increased velocity?