Page 380 - Libro 2
P. 380
360
PART 5 — ABDOMINAL
Figure 23-21 A renal artery stenosis (same patient as in Fig. 23-18). A pulsed Doppler tracing demonstrating distal poststenotic turbulence.
a low velocity signal. The Doppler signal of the artery feeding the AVF will have high velocity in both systole and end diastole, whereas the draining vein will dem- onstrate a pulsatile, relatively high velocity waveform that may even resemble an arterial signal close to the AVF (Fig. 23-23).
A PSA will be visualized on grayscale imaging as an anechoic rounded area within the renal paren- chyma, which will fill in with color in a swirling pattern (termed the “yin-yang” sign), which is flow heading toward the transducer as it enters the PSA in half the PSA and with reversed flow seen exiting the PSA in the other half (Figs. 23-24 through 23-26). A Doppler tracing obtained from the neck of the PSA where it joins the native artery will display a typi- cal “to-and-fro” Doppler pattern with flow heading
Figure 23-22 An arteriovenous fistula (AVF). A duplex Doppler image from a patient status postrenal biopsy demonstrating a soft tissue color bruit, increased systolic and diastolic flow, as well as turbulence from an AVF at the lower pole of the transplanted kidney.
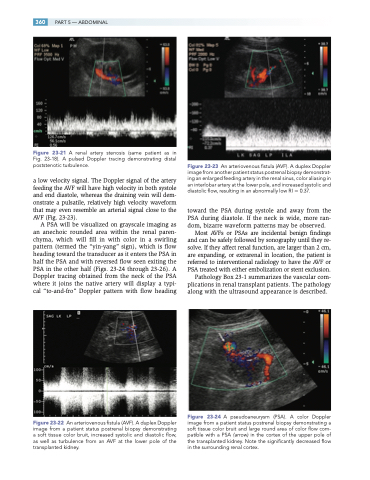
Figure 23-23 An arteriovenous fistula (AVF). A duplex Doppler image from another patient status postrenal biopsy demonstrat- ing an enlarged feeding artery in the renal sinus, color aliasing in an interlobar artery at the lower pole, and increased systolic and diastolic flow, resulting in an abnormally low RI 0.37.
toward the PSA during systole and away from the PSA during diastole. If the neck is wide, more ran- dom, bizarre waveform patterns may be observed.
Most AVFs or PSAs are incidental benign findings and can be safely followed by sonography until they re- solve. If they affect renal function, are larger than 2 cm, are expanding, or extrarenal in location, the patient is referred to interventional radiology to have the AVF or PSA treated with either embolization or stent exclusion.
Pathology Box 23-1 summarizes the vascular com- plications in renal transplant patients. The pathology along with the ultrasound appearance is described.
Figure 23-24 A pseudoaneurysm (PSA). A color Doppler image from a patient status postrenal biopsy demonstrating a soft tissue color bruit and large round area of color flow com- patible with a PSA (arrow) in the cortex of the upper pole of the transplanted kidney. Note the significantly decreased flow in the surrounding renal cortex.