Page 381 - Libro 2
P. 381
23 — Evaluation of Kidney and Liver Transplants 361
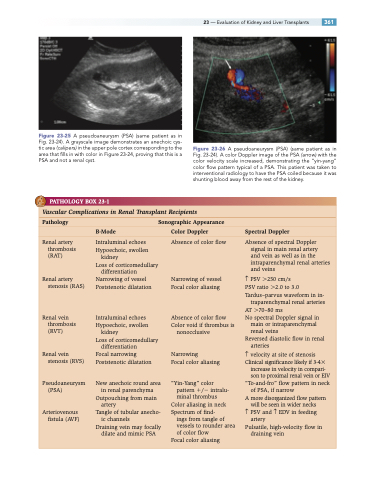
Figure 23-25 A pseudoaneurysm (PSA) (same patient as in Fig. 23-24). A grayscale image demonstrates an anechoic cys- tic area (calipers) in the upper pole cortex corresponding to the area that fills in with color in Figure 23-24, proving that this is a PSA and not a renal cyst.
Figure 23-26 A pseudoaneurysm (PSA) (same patient as in Fig. 23-24). A color Doppler image of the PSA (arrow) with the color velocity scale increased, demonstrating the “yin-yang” color flow pattern typical of a PSA. This patient was taken to interventional radiology to have the PSA coiled because it was shunting blood away from the rest of the kidney.
PATHOLOGY BOX 23-1
Vascular Complications in Renal Transplant Recipients
Pathology Sonographic Appearance
B-Mode Color Doppler Spectral Doppler
Renal artery thrombosis (RAT)
Renal artery stenosis (RAS)
Renal vein thrombosis (RVT)
Renal vein stenosis (RVS)
Pseudoaneurysm (PSA)
Arteriovenous fistula (AVF)
Intraluminal echoes Hypoechoic, swollen
kidney
Loss of corticomedullary
differentiation Narrowing of vessel Poststenotic dilatation
Intraluminal echoes Hypoechoic, swollen
kidney
Loss of corticomedullary
differentiation
Focal narrowing Poststenotic dilatation
New anechoic round area in renal parenchyma Outpouching from main
artery
Tangle of tubular anecho-
ic channels
Draining vein may focally
dilate and mimic PSA
Absence of color flow
Narrowing of vessel Focal color aliasing
Absence of color flow Color void if thrombus is
nonocclusive
Narrowing
Focal color aliasing
“Yin-Yang” color pattern / intralu- minal thrombus
Color aliasing in neck Spectrum of find-
ings from tangle of vessels to rounder area of color flow
Absence of spectral Doppler signal in main renal artery
and vein as well as in the intraparenchymal renal arteries and veins
↑ PSV 250 cm/s
PSV ratio 2.0 to 3.0 Tardus–parvus waveform in in-
traparenchymal renal arteries AT 70–80 ms
No spectral Doppler signal in
main or intraparenchymal
renal veins
Reversed diastolic flow in renal
arteries
↑ velocity at site of stenosis Clinical significance likely if 3-4
increase in velocity in compari-
son to proximal renal vein or EIV “To-and-fro” flow pattern in neck
of PSA, if narrow
A more disorganized flow pattern
will be seen in wider necks ↑ PSV and ↑ EDV in feeding
artery
Pulsatile, high-velocity flow in draining vein
Focal color aliasing