Page 122 - Medical Parasitology_ A Textbook ( PDFDrive )
P. 122
Other Types of Nematodes Infecting Humans 115
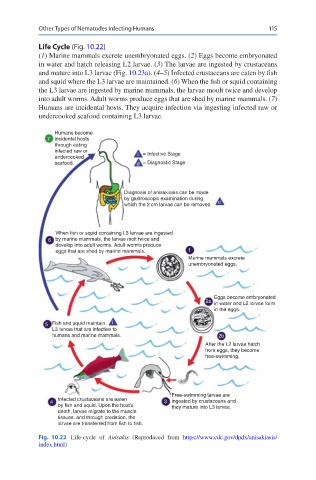
Life Cycle (Fig. 10.22)
(1) Marine mammals excrete unembryonated eggs. (2) Eggs become embryonated
in water and hatch releasing L2 larvae. (3) The larvae are ingested by crustaceans
and mature into L3 larvae (Fig. 10.23a). (4–5) Infected crustaceans are eaten by fish
and squid where the L3 larvae are maintained. (6) When the fish or squid containing
the L3 larvae are ingested by marine mammals, the larvae moult twice and develop
into adult worms. Adult worms produce eggs that are shed by marine mammals. (7)
Humans are incidental hosts. They acquire infection via ingesting infected raw or
undercooked seafood containing L3 larvae.
Humans become
7 incidental hosts
through eating
infected raw or i = Infective Stage
undercooked
seafood. d = Diagnostic Stage
Diagnosis of anisakiasis can be made
by gastroscopic examination during
which the 2 cm larvae can be removed. d
When fish or squid containing L3 larvae are ingested
6 by marine mammals, the larvae molt twice and
develop into adult worms. Adult worms produce
eggs that are shed by marine mammals. 1
Marine mammals excrete
unembryonated eggs.
Eggs become embryonated
2a in water and L2 larvae form
in the eggs.
5 Fish and squid maintain i
L3 larvae that are infective to
humans and marine mammals. 2b
After the L2 larvae hatch
from eggs, they become
free-swimming.
Free-swimming larvae are
4 Infected crustaceans are eaten 3 ingested by crustaceans and
by fish and squid. Upon the host’s they mature into L3 larvae.
death, larvae migrate to the muscle
tissues, and through predation, the
larvae are transferred from fish to fish.
Fig. 10.22 Life-cycle of Anisakis (Reproduced from https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/anisakiasis/
index.html)