Page 127 - Medical Parasitology_ A Textbook ( PDFDrive )
P. 127
120 11 Cestodes: Tapeworms
Infected crustacean ingested
by small freshwater fish. Predator fish eats
Procercoid larva released from 6 infected small fish
crustacean, develops into
plerocercoid larva 5 i
Procercoid i = Infective Stage
larvae in body Human ingests 7 d = Diagnostic
cavity of Stage
crustaceans raw or undercooked,
4 infected fish
scolex
8
Coracidia hatch Adults in small
from eggs and are intestine
ingested by 3
crustaceans.
d Proglottids release
2 Eggs embryonate 1 Unembryonated eggs 9 immature eggs
in water passed in faeces
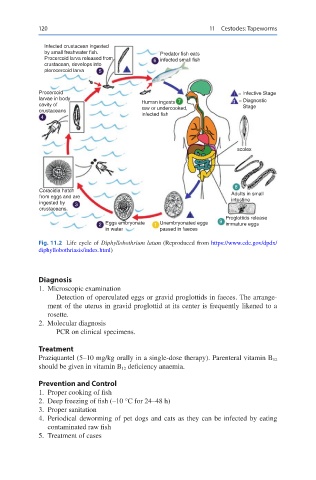
Fig. 11.2 Life cycle of Diphyllobothrium latum (Reproduced from https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/
diphyllobothriasis/index.html)
Diagnosis
1. Microscopic examination
Detection of operculated eggs or gravid proglottids in faeces. The arrange-
ment of the uterus in gravid proglottid at its center is frequently likened to a
rosette.
2. Molecular diagnosis
PCR on clinical specimens.
Treatment
Praziquantel (5–10 mg/kg orally in a single-dose therapy). Parenteral vitamin B 12
should be given in vitamin B 12 deficiency anaemia.
Prevention and Control
1. Proper cooking of fish
2. Deep freezing of fish (–10 °C for 24–48 h)
3. Proper sanitation
4. Periodical deworming of pet dogs and cats as they can be infected by eating
contaminated raw fish
5. Treatment of cases