Page 132 - Medical Parasitology_ A Textbook ( PDFDrive )
P. 132
Cyclophyllidean Tapeworms 125
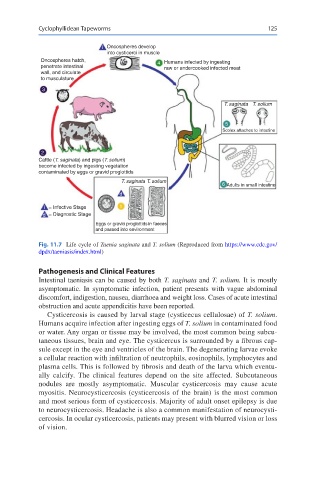
i Oncospheres develop
into cysticerci in muscle
Oncospheres hatch, 4 Humans infected by ingesting
penetrate intestinal raw or undercooked infected meat
wall, and circulate
to musculature
3
T. saginata T. solium
5
Scolex attaches to intestine
2
Cattle (T. saginata) and pigs (T. solium)
become infected by ingesting vegetation
contaminated by eggs or gravid proglottids
T. saginata T. solium
6 Adults in small intestine
d
i = Infective Stage 1
d = Diagnostic Stage
Eggs or gravid proglottids in faeces
and passed into environment
Fig. 11.7 Life cycle of Taenia saginata and T. solium (Reproduced from https://www.cdc.gov/
dpdx/taeniasis/index.html)
Pathogenesis and Clinical Features
Intestinal taeniasis can be caused by both T. saginata and T. solium. It is mostly
asymptomatic. In symptomatic infection, patient presents with vague abdominal
discomfort, indigestion, nausea, diarrhoea and weight loss. Cases of acute intestinal
obstruction and acute appendicitis have been reported.
Cysticercosis is caused by larval stage (cysticecus cellulosae) of T. solium.
Humans acquire infection after ingesting eggs of T. solium in contaminated food
or water. Any organ or tissue may be involved, the most common being subcu-
taneous tissues, brain and eye. The cysticercus is surrounded by a fibrous cap-
sule except in the eye and ventricles of the brain. The degenerating larvae evoke
a cellular reaction with infiltration of neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes and
plasma cells. This is followed by fibrosis and death of the larva which eventu-
ally calcify. The clinical features depend on the site affected. Subcutaneous
nodules are mostly asymptomatic. Muscular cysticercosis may cause acute
myositis. Neurocysticercosis (cysticercosis of the brain) is the most common
and most serious form of cysticercosis. Majority of adult onset epilepsy is due
to neurocysticercosis. Headache is also a common manifestation of neurocysti-
cercosis. In ocular cysticercosis, patients may present with blurred vision or loss
of vision.