Page 18 - Medical Parasitology_ A Textbook ( PDFDrive )
P. 18
10 3 Amoebae
a b
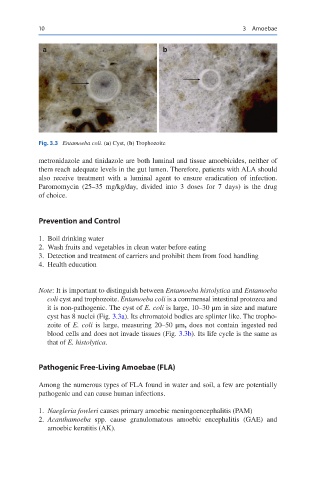
Fig. 3.3 Entamoeba coli. (a) Cyst, (b) Trophozoite
metronidazole and tinidazole are both luminal and tissue amoebicides, neither of
them reach adequate levels in the gut lumen. Therefore, patients with ALA should
also receive treatment with a luminal agent to ensure eradication of infection.
Paromomycin (25–35 mg/kg/day, divided into 3 doses for 7 days) is the drug
of choice.
Prevention and Control
1. Boil drinking water
2. Wash fruits and vegetables in clean water before eating
3. Detection and treatment of carriers and prohibit them from food handling
4. Health education
Note: It is important to distinguish between Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba
coli cyst and trophozoite. Entamoeba coli is a commensal intestinal protozoa and
it is non- pathogenic. The cyst of E. coli is large, 10–30 μm in size and mature
cyst has 8 nuclei (Fig. 3.3a). Its chromatoid bodies are splinter like. The tropho-
zoite of E. coli is large, measuring 20–50 μm, does not contain ingested red
blood cells and does not invade tissues (Fig. 3.3b). Its life cycle is the same as
that of E. histolytica.
Pathogenic Free-Living Amoebae (FLA)
Among the numerous types of FLA found in water and soil, a few are potentially
pathogenic and can cause human infections.
1. Naegleria fowleri causes primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
2. Acanthamoeba spp. cause granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE) and
amoebic keratitis (AK).