Page 87 - Medical Parasitology_ A Textbook ( PDFDrive )
P. 87
80 10 Nematodes: Roundworms
Table 10.1 Classification of nematodes of medical importance based on habitat
Habitat of adult nematode Nematode
Small intestine 1. Ascaris lumbricoides
2. Strongyloides stercoralis
3. Hookworm
4. Trichinella spiralis
Large intestine 1. Trichuris trichiura
2. Enterobius vermicularis
Lymphatic 1. Wuchereria bancrofti
2. Brugia malayi
Subcutaneous 1. Loa loa
2. Onchocerca volvulus
a b
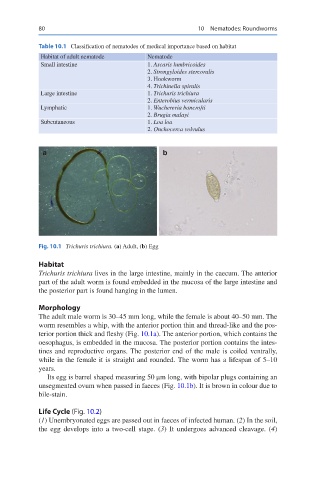
Fig. 10.1 Trichuris trichiura. (a) Adult, (b) Egg
Habitat
Trichuris trichiura lives in the large intestine, mainly in the caecum. The anterior
part of the adult worm is found embedded in the mucosa of the large intestine and
the posterior part is found hanging in the lumen.
Morphology
The adult male worm is 30–45 mm long, while the female is about 40–50 mm. The
worm resembles a whip, with the anterior portion thin and thread-like and the pos-
terior portion thick and fleshy (Fig. 10.1a). The anterior portion, which contains the
oesophagus, is embedded in the mucosa. The posterior portion contains the intes-
tines and reproductive organs. The posterior end of the male is coiled ventrally,
while in the female it is straight and rounded. The worm has a lifespan of 5–10
years.
Its egg is barrel shaped measuring 50 μm long, with bipolar plugs containing an
unsegmented ovum when passed in faeces (Fig. 10.1b). It is brown in colour due to
bile-stain.
Life Cycle (Fig. 10.2)
(1) Unembryonated eggs are passed out in faeces of infected human. (2) In the soil,
the egg develops into a two-cell stage. (3) It undergoes advanced cleavage. (4)