Page 184 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 184
170 SECTION II Autonomic Drugs
β antagonists in insulin-dependent diabetic patients who are sub- compared with that in diabetics receiving nonselective β-adrenoceptor
ject to frequent hypoglycemic reactions if alternative therapies are antagonists. There is considerable potential benefit from these drugs
available. Beta -selective antagonists offer some advantage in these in diabetics after a myocardial infarction, so the balance of risk versus
1
patients, since the rate of recovery from hypoglycemia may be faster benefit must be evaluated in individual patients.
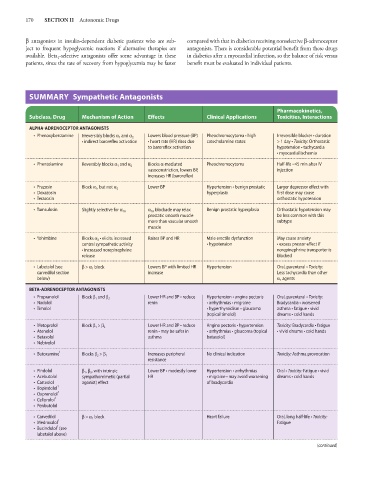
SUMMARY Sympathetic Antagonists
Pharmacokinetics,
Subclass, Drug Mechanism of Action Effects Clinical Applications Toxicities, Interactions
ALPHA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS
• Phenoxybenzamine Irreversibly blocks α 1 and α 2 Lowers blood pressure (BP) Pheochromocytoma • high Irreversible blocker • duration
• indirect baroreflex activation • heart rate (HR) rises due catecholamine states > 1 day • Toxicity: Orthostatic
to baroreflex activation hypotension • tachycardia
• myocardial ischemia
• Phentolamine Reversibly blocks α 1 and α 2 Blocks α-mediated Pheochromocytoma Half-life ~45 min after IV
vasoconstriction, lowers BP, injection
increases HR (baroreflex)
• Prazosin Block α 1 , but not α 2 Lower BP Hypertension • benign prostatic Larger depressor effect with
• Doxazosin hyperplasia first dose may cause
• Terazosin orthostatic hypotension
• Tamsulosin Slightly selective for α 1A α 1A blockade may relax Benign prostatic hyperplasia Orthostatic hypotension may
prostatic smooth muscle be less common with this
more than vascular smooth subtype
muscle
• Yohimbine Blocks α 2 • elicits increased Raises BP and HR Male erectile dysfunction May cause anxiety
central sympathetic activity • hypotension • excess pressor effect if
• increased norepinephrine norepinephrine transporter is
release blocked
• Labetalol (see β > α 1 block Lowers BP with limited HR Hypertension Oral, parenteral • Toxicity:
carvedilol section increase Less tachycardia than other
below) α 1 agents
BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS
• Propranolol Block β 1 and β 2 Lower HR and BP • reduce Hypertension • angina pectoris Oral, parenteral • Toxicity:
• Nadolol renin • arrhythmias • migraine Bradycardia • worsened
• Timolol • hyperthyroidism • glaucoma asthma • fatigue • vivid
(topical timolol) dreams • cold hands
• Metoprolol Block β 1 > β 2 Lower HR and BP • reduce Angina pectoris • hypertension Toxicity: Bradycardia • fatigue
• Atenolol renin • may be safer in • arrhythmias • glaucoma (topical • vivid dreams • cold hands
• Betaxolol asthma betaxolol)
• Nebivolol
• Butoxamine 1 Blocks β 2 > β 1 Increases peripheral No clinical indication Toxicity: Asthma provocation
resistance
• Pindolol β 1 , β 2 , with intrinsic Lower BP • modestly lower Hypertension • arrhythmias Oral • Toxicity: Fatigue • vivid
• Acebutolol sympathomimetic (partial HR • migraine • may avoid worsening dreams • cold hands
• Carteolol agonist) effect of bradycardia
• Bopindolol 1
• Oxprenolol 1
• Celiprolol 1
• Penbutolol
• Carvedilol β > α 1 block Heart failure Oral, long half-life • Toxicity:
• Medroxalol 1 Fatigue
1
• Bucindolol (see
labetalol above)
(continued)