Page 78 - parasitology for medical and clinical laboratoryprofessionals
P. 78
58 CHAPTER 3
invaluable when faced with the task of identifying proto-
zoa of the human gastrointestinal tract.
BLASTOCYSTIS HOMINIS
Blastocystis is a single-celled parasite that infects the Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
gastrointestinal tract of humans and other animals. Many
different species of the Blastocystis genus exist and are
prevalent in not only humans but also are found to infect
farm animals, birds, various rodents, amphibians, rep-
tiles, fish, and even insects such as cockroaches. This
provides for a wide variety of reservoirs from which
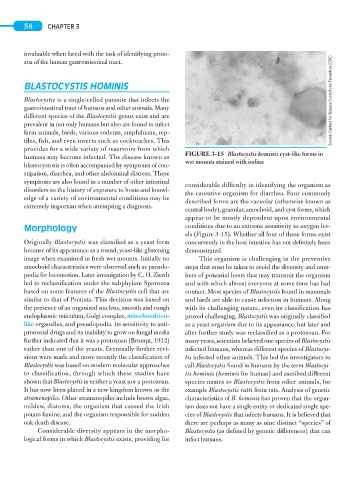
FIGURE 3-15 Blastocystis hominis cyst-like forms in
humans may become infected. The disease known as
wet mounts stained with iodine
blastocystosis is often accompanied by symptoms of con-
stipation, diarrhea, and other abdominal distress. These
symptoms are also found in a number of other intestinal considerable difficulty in identifying the organism as
disorders so the history of exposure to hosts and knowl-
the causative organism for diarrhea. Four commonly
edge of a variety of environmental conditions may be described forms are the vacuolar (otherwise known as
extremely important when attempting a diagnosis.
central body), granular, amoeboid, and cyst forms, which
appear to be mostly dependent upon environmental
Morphology conditions due to an extreme sensitivity to oxygen lev-
els (Figure 3-15). Whether all four of these forms exist
Originally Blastocystis was classified as a yeast form concurrently in the host intestine has not definitely been
because of its appearance as a round, yeast-like glistening demonstrated.
image when examined in fresh wet mounts. Initially no This organism is challenging in the preventive
amoeboid characteristics were observed such as pseudo- steps that must be taken to avoid the diversity and num-
podia for locomotion. Later investigation by C. H. Zierdt bers of potential hosts that may transmit the organism
led to reclassification under the subphylum Sporozoa and with which almost everyone at some time has had
based on some features of the Blastocystis cell that are contact. Most species of Blastocystis found in mammals
similar to that of Protista. This decision was based on and birds are able to cause infection in humans. Along
the presence of an organized nucleus, smooth and rough with its challenging nature, even its classification has
endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, mitochondrion- proved challenging. Blastocystis was originally classified
like organelles, and pseudopodia. Its sensitivity to anti- as a yeast organism due to its appearance, but later and
protozoal drugs and its inability to grow on fungal media after further study was reclassified as a protozoan. For
further indicated that it was a protozoan (Brumpt, 1912) many years, scientists believed one species of Blastocystis
rather than one of the yeasts. Eventually further revi- infected humans, whereas different species of Blastocys-
sions were made and more recently the classification of tis infected other animals. This led the investigators to
Blastocystis was based on modern molecular approaches call Blastocystis found in humans by the term Blastocys-
to classification, through which these studies have tis hominis (hominis for human) and ascribed different
shown that Blastocystis is neither a yeast nor a protozoan. species names to Blastocystis from other animals, for
It has now been placed in a new kingdom known as the example Blastocystis ratti from rats. Analysis of genetic
stramenopiles. Other stramenopiles include brown algae, characteristics of B. hominis has proven that the organ-
mildew, diatoms, the organism that caused the Irish ism does not have a single entity or dedicated single spe-
potato famine, and the organism responsible for sudden cies of Blastocystis that infects humans. It is believed that
oak death disease. there are perhaps as many as nine distinct “species” of
Considerable diversity appears in the morpho- Blastocystis (as defined by genetic differences) that can
logical forms in which Blastocystis exists, providing for infect humans.