Page 164 - Pharmacognosy 2 PG303
P. 164
Pharmacognosy-2 (PG303) Level 2 Clinical Pharmacy-Pharm D
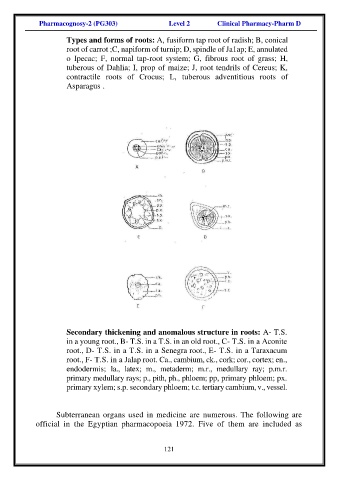
Types and forms of roots: A, fusiform tap root of radish; B, conical
root of carrot ;C, napiform of turnip; D, spindle of Ja1ap; E, annulated
o Ipecac; F, normal tap-root system; G, fibrous root of grass; H,
tuberous of Dahlia; I, prop of maize; J, root tendrils of Cereus; K,
contractile roots of Crocus; L, tuberous adventitious roots of
Asparagus .
Secondary thickening and anomalous structure in roots: A- T.S.
in a young root., B- T.S. in a T.S. in an old root., C- T.S. in a Aconite
root., D- T.S. in a T.S. in a Senegra root., E- T.S. in a Taraxacum
root., F- T.S. in a Jalap root. Ca., cambium, ck., cork; cor., cortex; en.,
endodermis; la., latex; m., metaderm; m.r., medullary ray; p.m.r.
primary medullary rays; p., pith, ph., phloem; pp, primary phloem; px.
primary xylem; s.p. secondary phloem; t.c. tertiary cambium, v., vessel.
Subterranean organs used in medicine are numerous. The following are
official in the Egyptian pharmacopoeia 1972. Five of them are included as
121