Page 123 - Enzymes in Tropical Soils
P. 123
Enzymes in Tropical Soils 111
o
incubated at 30 C for 1 hour, the enzymatic reaction is stopped by an addition of a
1 mL 1 M NaOH solution, and continued by an addition of a 4 mL 1 M CaCl 2 solution
to extract p-nitrophenol from soil colloids. The concentration of p-nitrophenol is
determined at 400 nm using UV-Vis spectrophotometer.
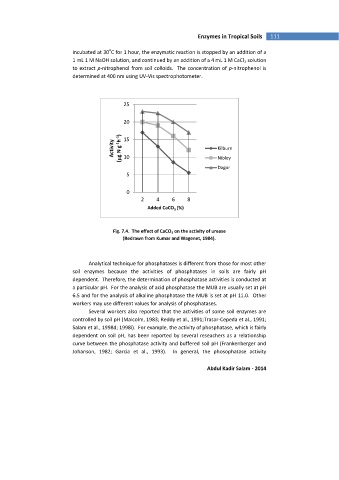
25
20
Activity (mg N g -1 h -1 ) 15 Kilburn
10
Nibley
Dagor
5
0
2 4 6 8
Added CaCO (%)
3
Fig. 7.4. The effect of CaCO 3 on the activity of urease
(Redrawn from Kumar and Wagenet, 1984).
Analytical technique for phosphatases is different from those for most other
soil enzymes because the activities of phosphatases in soils are fairly pH
dependent. Therefore, the determination of phosphatase activities is conducted at
a particular pH. For the analysis of acid phosphatase the MUB are usually set at pH
6.5 and for the analysis of alkaline phosphatase the MUB is set at pH 11.0. Other
workers may use different values for analysis of phosphatases.
Several workers also reported that the activities of some soil enzymes are
controlled by soil pH (Malcolm, 1983; Reddy et al., 1991;Trasar-Cepeda et al., 1991;
Salam et al., 1998d; 1998i). For example, the activity of phosphatase, which is fairly
dependent on soil pH, has been reported by several reseachers as a relationship
curve between the phosphatase activity and buffered soil pH (Frankenberger and
Johanson, 1982; Garcia et al., 1993). In general, the phosophatase activity
Abdul Kadir Salam - 2014