Page 154 - Enzymes in Tropical Soils
P. 154
142 Enzymes In Tropical Soils
The exception to the above pattern is for Cu and Zn in andic soils or
Andisols, which contain colloids that are susceptible to liming. In this soils, lime
destroys allophane minerals which are unstable (Paterson et al., 1991; Salam et al.,
1997h; 1997j). Salam et al. (1999h) showed that the negative effect of Pb
electonics industrial waste planted with corn, amaranth, or gree kyllinga was
attenuated by liming.
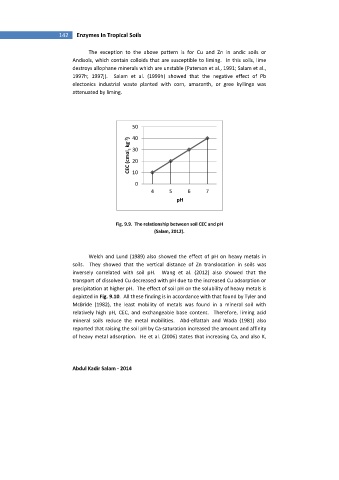
50
CEC (cmol c kg -1 ) 30
40
20
10
0
4 5 6 7
pH
Fig. 9.9. The relationship between soil CEC and pH
(Salam, 2012).
Welch and Lund (1989) also showed the effect of pH on heavy metals in
soils. They showed that the vertical distance of Zn translocation in soils was
inversely correlated with soil pH. Wang et al. (2012) also showed that the
transport of dissolved Cu decreased with pH due to the increased Cu adsorption or
precipitation at higher pH. The effect of soil pH on the solubility of heavy metals is
depicted in Fig. 9.10. All these finding is in accordance with that found by Tyler and
McBride (1982), the least mobility of metals was found in a mineral soil with
relatively high pH, CEC, and exchangeable base content. Therefore, liming acid
mineral soils reduce the metal mobilities. Abd-elfattah and Wada (1981) also
reported that raising the soil pH by Ca-saturation increased the amount and affinity
of heavy metal adsorption. He et al. (2006) states that increasing Ca, and also K,
Abdul Kadir Salam - 2014