Page 122 - Ilmu Tanah
P. 122
The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds 109
significantly increased in soil covered with grasses. Salam et al. (1998b) also report
that land-use conversion from the primary and secondary forest to agriculture
lands drastically decreased the soil enzymatic activities. Jha et al. (1992) also
report that the activity of phosphatase was higher in undisturbed forest soils
compared to those in soils that had been disturbed. All these data indicate that the
activities of soil enzymes are related to the contents of soil organic C controlled by
plant covers.
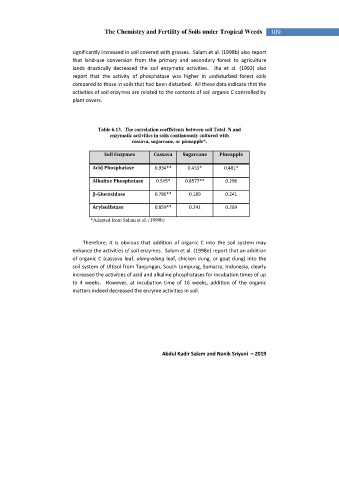
Table 6.13. The correlation coefficients between soil Total N and
enzymatic activities in soils continuously cultured with
cassava, sugarcane, or pineapple*.
Soil Enzymes Cassava Sugarcane Pineapple
Acid Phosphatase 0.934** 0.455* 0.481*
Alkaline Phosphatase 0.545* 0.8577** 0.296
-Glucosidase 0.786** 0.189 0.241
Arylsulfatase 0.859** 0.241 0.269
*Adapted from Salam et al. (1999b)
Therefore, it is obvious that addition of organic C into the soil system may
enhance the activities of soil enzymes. Salam et al. (1998e) report that an addition
of organic C (cassava leaf, alang-alang leaf, chicken dung, or goat dung) into the
soil system of Ultisol from Tanjungan, South Lampung, Sumatra, Indonesia, clearly
increased the activities of acid and alkaline phosphatases for incubation times of up
to 4 weeks. However, at incubation time of 16 weeks, addition of the organic
matters indeed decreased the enzyme activities in soil.
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019