Page 128 - Ilmu Tanah
P. 128
The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds 115
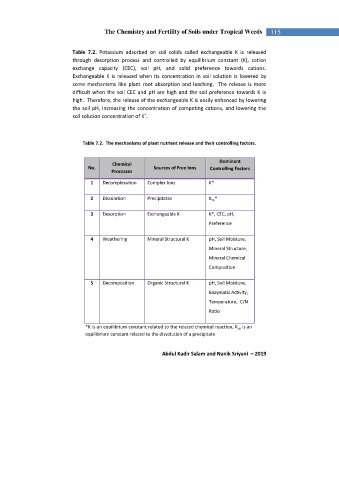
Table 7.2. Potassium adsorbed on soil solids called exchangeable K is released
through desorption process and controlled by equilibrium constant (K), cation
exchange capacity (CEC), soil pH, and solid preference towards cations.
Exchangeable K is released when its concentration in soil solution is lowered by
some mechanisms like plant root absorption and leaching. The release is more
difficult when the soil CEC and pH are high and the soil preference towards K is
high. Therefore, the release of the exchangeable K is easily enhanced by lowering
the soil pH, increasing the concentration of competing cations, and lowering the
+
soil solution concentration of K .
Table 7.2. The mechanisms of plant nutrient release and their controlling factors.
Dominant
Chemical
No. Sources of Free Ions Controlling Factors
Processes
1 Decomplexation Complex Ions K*
2 Dissolution Precipitates K sp *
3 Desorption Exchangeable K K*, CEC, pH,
Preference
4 Weathering Mineral Structural K pH, Soil Moisture,
Mineral Structure,
Mineral Chemical
Composition
5 Decomposition Organic Structural K pH, Soil Moisture,
Enzymatic Activity,
Temperature, C/N
Ratio
*K is an equilibrium constant related to the related chemical reaction, K sp is an
equilibrium constant related to the dissolution of a precipitate
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019