Page 90 - Ilmu Tanah
P. 90
The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds 77
sulfur powder to manage particular plant deseases at low pH. This practice has
acidified the soils to relatively low values (Salam et al., 1999b).
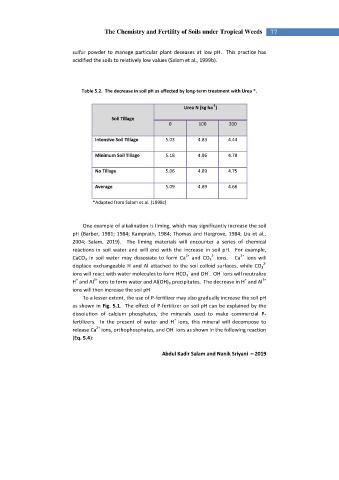
Table 5.2. The decrease in soil pH as affected by long-term treatment with Urea *.
-1
Urea N (kg ha )
Soil Tillage
0 100 200
Intensive Soil Tillage 5.03 4.83 4.44
Minimum Soil Tillage 5.18 4.96 4.78
No Tillage 5.06 4.89 4.75
Average 5.09 4.89 4.66
*Adapted from Salam et al. (1998c)
One example of alkalination is liming, which may significantly increase the soil
pH (Barber, 1981; 1984; Kamprath, 1984; Thomas and Hargrove, 1984; Liu et al.,
2004; Salam, 2019). The liming materials will encounter a series of chemical
reactions in soil water and will end with the increase in soil pH. For example,
2+ 2- 2+
CaCO 3 in soil water may dissosiate to form Ca and CO 3 ions. Ca ions will
2-
displace exchangeable H and Al attached to the soil colloid surfaces, while CO 3
- - -
ions will react with water molecules to form HCO 3 and OH . OH ions will neutralize
+ 3+ + 3+
H and Al ions to form water and Al(OH) 3 precipitates. The decrease in H and Al
ions will then increase the soil pH
To a lesser extent, the use of P-fertilizer may also gradually increase the soil pH
as shown in Fig. 5.1. The effect of P-fertilizer on soil pH can be explained by the
dissolution of calcium phosphates, the minerals used to make commercial P-
+
fertilizers. In the present of water and H ions, this mineral will decompose to
-
2+
release Ca ions, orthophosphates, and OH ions as shown in the following reaction
(Eq. 5.4):
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019