Page 91 - Ilmu Tanah
P. 91
78 The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds
-
+
2+
-
Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 + 2 H 2 O + 2 H 3 Ca + 2 H 2 PO 4 + 2 OH ....... Eq. 5.4
+ -
This decomposition reaction consumes H ions and produces OH ions; therefore, it
+
increases the soil pH. In general, the higher the concentrations of H ions or the
lower the soil pH, the more intensive the decomposition of calcium phosphates.
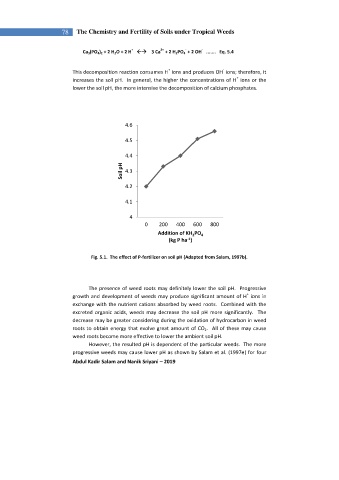
4.6
4.5
4.4
Soil pH 4.3
4.2
4.1
4
0 200 400 600 800
Addition of KH PO 4
2
-1
(kg P ha )
Fig. 5.1. The effect of P-fertilizer on soil pH (Adapted from Salam, 1997b).
The presence of weed roots may definitely lower the soil pH. Progressive
+
growth and development of weeds may produce significant amount of H ions in
exchange with the nutrient cations absorbed by weed roots. Combined with the
excreted organic acids, weeds may decrease the soil pH more significantly. The
decrease may be greater considering during the oxidation of hydrocarbon in weed
roots to obtain energy that evolve great amount of CO 2 . All of these may cause
weed roots become more effective to lower the ambient soil pH.
However, the resulted pH is dependent of the particular weeds. The more
progressive weeds may cause lower pH as shown by Salam et al. (1997e) for four
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019