Page 146 - Ilmu Tanah Book
P. 146
The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds 133
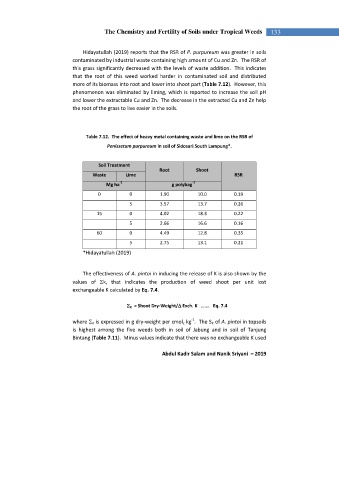
Hidayatullah (2019) reports that the RSR of P. purpureum was greater in soils
contaminated by industrial waste containing high amount of Cu and Zn. The RSR of
this grass significantly decreased with the levels of waste addition. This indicates
that the root of this weed worked harder in contaminated soil and distributed
more of its biomass into root and lower into shoot part (Table 7.12). However, this
phenomenon was eliminated by liming, which is reported to increase the soil pH
and lower the extractable Cu and Zn. The decrease in the extracted Cu and Zn help
the root of the grass to live easier in the soils.
Table 7.12. The effect of heavy metal containing waste and lime on the RSR of
Penissetum purpureum in soil of Sidosari South Lampung*.
Soil Treatment
Root Shoot
Waste Lime RSR
-1 -1
Mg ha g polybag
0 0 1.90 10.0 0.19
5 3.57 13.7 0.26
15 0 4.02 18.3 0.22
5 2.66 16.6 0.16
60 0 4.49 12.8 0.35
5 2.75 13.1 0.21
*Hidayatullah (2019)
The effectiveness of A. pintoi in inducing the release of K is also shown by the
values of k, that indicates the production of weed shoot per unit lost
exchangeable K calculated by Eq. 7.4.
K = Shoot Dry-Weight/ Exch. K ……. Eq. 7.4
-1
where K is expressed in g dry-weight per cmol c kg . The S K of A. pintoi in topsoils
is highest among the five weeds both in soil of Jabung and in soil of Tanjung
Bintang (Table 7.11). Minus values indicate that there was no exchangeable K used
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019