Page 94 - Ilmu Tanah Book
P. 94
The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds 81
obvious that the plant-induced changes to soil enzyme activities are driven primarily by
readily available, labile carbon provided by root turnover and root exudation rather than by
aboveground detrital inputs.
200
Activity (g p-nitrophenol g -1 h -1 ) 140
180
160
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
Imperata Amaranthus Amaranthus Cyperus
cylindrica tricolor spinosus kyllingia
Acid Phosphatase Alkaline Phosphatase
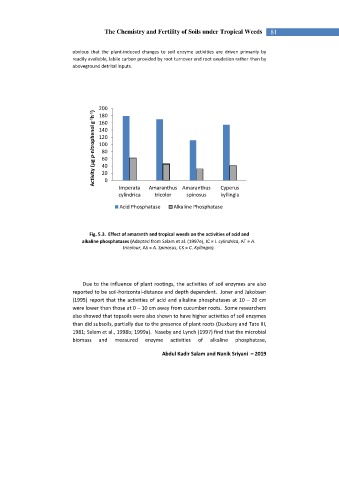
Fig. 5.3. Effect of amaranth and tropical weeds on the activities of acid and
alkaline phosphatases (Adapted from Salam et al. (1997e), IC = I. cylindrica, AT = A.
tricolour, AS = A. Spinosus, CK = C. Kyllingia).
Due to the influence of plant rootings, the activities of soil enzymes are also
reported to be soil-horizontal-distance and depth dependent. Joner and Jakobsen
(1995) report that the activities of acid and alkaline phosphatases at 10 – 20 cm
were lower than those at 0 – 10 cm away from cucumber roots. Some researchers
also showed that topsoils were also shown to have higher activities of soil enzymes
than did subsoils, partially due to the presence of plant roots (Duxbury and Tate III,
1981; Salam et al., 1998b; 1999a). Naseby and Lynch (1997) find that the microbial
biomass and measured enzyme activities of alkaline phosphatase,
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019