Page 95 - Ilmu Tanah Book
P. 95
82 The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds
phosphodiesterase, arylsulfatase, and urease decreased with soil depth. However,
a close relationship between topsoil and subsoil enzymatic activities (Salam et al.,
1998b; 1999a; Salam et al., 2001) may to some extent indicate that enzymes are
produced in topsoils but may be partially leached through the soil profiles by
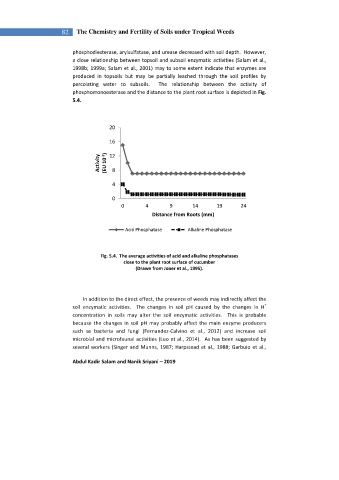
percolating water to subsoils. The relationship between the activity of
phosphomonoesterase and the distance to the plant root surface is depicted in Fig.
5.4.
20
16
Activity (EU 10 -3 ) 12
8
4
0
0 4 9 14 19 24
Distance from Roots (mm)
Acid Phosphatase Alkaline Phosphatase
Fig. 5.4. The average activities of acid and alkaline phosphatases
close to the plant root surface of cucumber
(Drawn from Joner et al., 1995).
In addition to the direct effect, the presence of weeds may indirectly affect the
+
soil enzymatic activities. The changes in soil pH caused by the changes in H
concentration in soils may alter the soil enzymatic activities. This is probable
because the changes in soil pH may probably affect the main enzyme producers
such as bacteria and fungi (Fernandez-Calvino et al., 2012) and increase soil
microbial and microfaunal activities (Luo et al., 2014). As has been suggested by
several workers (Singer and Munns, 1987; Harpstead et al., 1988; Garbuio et al.,
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019