Page 69 - Programmable Logic Controllers, Fifth Edition
P. 69
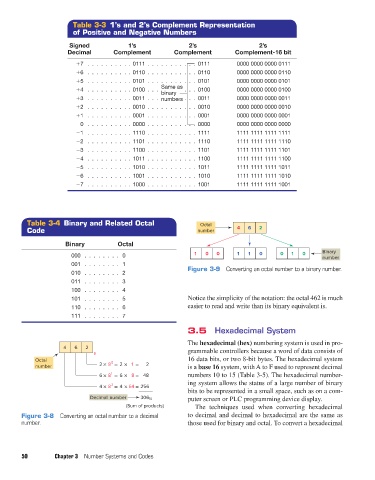
Table 3-3 1’s and 2’s Complement Representation
of Positive and Negative Numbers
Signed 1’s 2’s 2’s
Decimal Complement Complement Complement-16 bit
+7 0111 0111 0000 0000 0000 0111
+6 0110 0110 0000 0000 0000 0110
+5 0101 0101 0000 0000 0000 0101
Same as
+4 0100 0100 0000 0000 0000 0100
binary
+3 0011 0011 0000 0000 0000 0011
numbers
+2 0010 0010 0000 0000 0000 0010
+1 0001 0001 0000 0000 0000 0001
0 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
−1 1110 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
−2 1101 1110 1111 1111 1111 1110
−3 1100 1101 1111 1111 1111 1101
−4 1011 1100 1111 1111 1111 1100
−5 1010 1011 1111 1111 1111 1011
−6 1001 1010 1111 1111 1111 1010
−7 1000 1001 1111 1111 1111 1001
Table 3-4 Binary and Related Octal Octal
Code number 4 6 2
Binary Octal
000 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 Binary
number
001 1
Figure 3-9 Converting an octal number to a binary number.
010 2
011 3
100 4
101 5 Notice the simplicity of the notation: the octal 462 is much
110 6 easier to read and write than its binary equivalent is.
111 7
3.5 Hexadecimal System
The hexadecimal (hex) numbering system is used in pro-
4 6 2
8 grammable controllers because a word of data consists of
Octal 0 16 data bits, or two 8-bit bytes. The hexadecimal system
number 2 × 8 = 2 × 1 = 2 is a base 16 system, with A to F used to represent decimal
1
6 × 8 = 6 × 8 = 48 numbers 10 to 15 (Table 3-5). The hexadecimal number-
2
4 × 8 = 4 × 64 = 256 ing system allows the status of a large number of binary
bits to be represented in a small space, such as on a com-
Decimal number 306 10 puter screen or PLC programming device display.
(Sum of products) The techniques used when converting hexadecimal
Figure 3-8 Converting an octal number to a decimal to decimal and decimal to hexadecimal are the same as
number. those used for binary and octal. To convert a hexadecimal
50 Chapter 3 Number Systems and Codes
pet73842_ch03_046-060.indd 50 03/11/15 3:50 PM