Page 113 - Servo Motors and Industrial Control Theory
P. 113
6.3 Mathematical Model 107
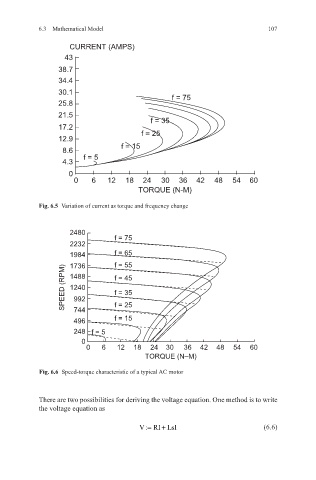
CURRENT (AMPS)
43
38.7
34.4
30.1 f = 75
25.8
21.5 f = 35
17.2
12.9 f = 25
8.6 f = 15
4.3 f = 5
0
0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60
TORQUE (N-M)
Fig. 6.5 Variation of current as torque and frequency change
2480
f = 75
2232
1984 f = 65
f = 55
1736
SPEED (RPM) 1488 f = 45
1240
f = 35
992
f = 25
744
496 f = 15
248 f = 5
0
0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60
TORQUE (N–M)
Fig. 6.6 Speed-torque characteristic of a typical AC motor
There are two possibilities for deriving the voltage equation. One method is to write
the voltage equation as
+
=
V : RI LsI (6.6)