Page 113 - ISCI’2017
P. 113
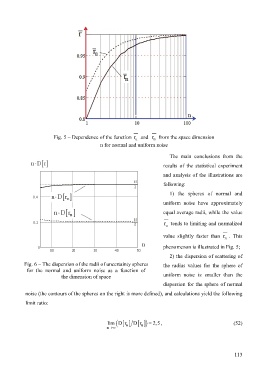
Fig. 5 – Dependence of the function r u and r n from the space dimension
n for normal and uniform noise
The main conclusions from the
results of the statistical experiment
and analysis of the illustrations are
following:
1) the spheres of normal and
uniform noise have approximately
equal average radii, while the value
r u tends to limiting and normalized
value slightly faster than r n . This
phenomenon is illustrated in Fig. 5;
2) the dispersion of scattering of
Fig. 6 – The dispersion of the radii of uncertainty spheres the radius values for the sphere of
for the normal and uniform noise as a function of
the dimension of space uniform noise is smaller than the
dispersion for the sphere of normal
noise (the contours of the spheres on the right is more defined), and calculations yield the following
limit ratio:
lim (D r n D r u , (52)
[ ] [ ]) 2,5=
n→∞
113