Page 23 - ISCI’2017
P. 23
4 Cartographic Analysis of MCRIM Results
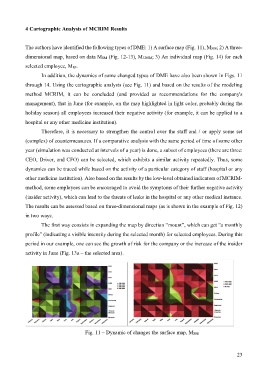
The authors have identified the following types of DME: 1) A surface map (Fig. 11), MSM; 2) A three-
dimensional map, based on data MSM (Fig. 12-13), M3DSM; 3) An individual map (Fig. 14) for each
selected employee, MID.
In addition, the dynamics of some changed types of DME have also been shown in Figs. 11
through 14. Using the cartographic analysis (see Fig. 11) and based on the results of the modeling
method MCRIM, it can be concluded (and provided as recommendations for the company's
management), that in June (for example, on the map highlighted in light color, probably during the
holiday season) all employees increased their negative activity (for example, it can be applied to a
hospital or any other medicine institution).
Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the control over the staff and / or apply some set
(complex) of countermeasures. If a comparative analysis with the same period of time of some other
year (simulation was conducted at intervals of a year) is done, a subset of employees (there are three:
CEO, Driver, and CFO) can be selected, which exhibits a similar activity repeatedly. Thus, some
dynamics can be traced while based on the activity of a particular category of staff (hospital or any
other medicine institution). Also based on the results by the low-level obtained indicators of MCRIM-
method, some employees can be encouraged to avoid the symptoms of their further negative activity
(insider activity), which can lead to the threats of leaks in the hospital or any other medical instance.
The results can be assessed based on three-dimensional maps (as is shown in the example of Fig. 12)
in two ways.
The first way consists in expanding the map by direction “mount”, which can get “a monthly
profile” (indicating a visible intensity during the selected month) for selected employees. During this
period in our example, one can see the growth of risk for the company or the increase of the insider
activity in June (Fig. 13a – the selected area).
Fig. 11 – Dynamic of changes the surface map, MSM
23