Page 103 - From GMS to LTE
P. 103
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) and EDGE 89
areas would enable operators to better fine‐tune their networks by enabling them to
control GSM and GPRS signaling messages independently.
If the mobile device detects after a cell change that the routing area is different from
that of the previous cell, it starts to perform a routing area update (RAU), which is similar
to a GSM location area update. In case the location area has changed as well, the mobile
device needs to perform both an LU and an RAU.
The advantage of the standby state for the network is the reduced signaling overhead
as not every cell change has to be reported. Thus, scarce resources on the RACH, the
AGCH and the PDTCH can be saved. For the mobile device, the advantage of
the standby state is that it can stop the continuous monitoring of the AGCH and only
infrequently monitor the PCH, as described in more detail below. Most operators have
set the PCH monitoring interval to around 1.5 seconds (e.g. 6–8 multiframes), which
helps to significantly reduce power consumption.
In the uplink direction, there is no difference between ready and standby states. If a
mobile device wants to send data while in standby state, it implicitly switches back to
ready state once the first frame is sent to the network.
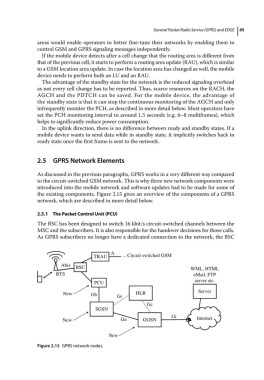
2.5 GPRS Network Elements
As discussed in the previous paragraphs, GPRS works in a very different way compared
to the circuit‐switched GSM network. This is why three new network components were
introduced into the mobile network and software updates had to be made for some of
the existing components. Figure 2.15 gives an overview of the components of a GPRS
network, which are described in more detail below.
2.5.1 The Packet Control Unit (PCU)
The BSC has been designed to switch 16 kbit/s circuit‐switched channels between the
MSC and the subscribers. It is also responsible for the handover decisions for those calls.
As GPRS subscribers no longer have a dedicated connection to the network, the BSC
A
TRAU ... Circuit switched GSM
Abis BSC WML, HTML
BTS eMail, FTP
PCU server etc.
New Gb Gr HLR Server
Gc
SGSN
Gi
New Gn GGSN Internet
New
Figure 2.15 GPRS network nodes.