Page 303 - From GMS to LTE
P. 303
Long Term Evolution (LTE) and LTE-Advanced Pro 289
to as VoLTE and is based on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) that was first introduced
with 3GPP Release 5. Many additions and enhancements were necessary over time.
However, when the first LTE networks appeared in practice, stable and fully functional
VoLTE systems were still not available. As a consequence, it was decided to continue
using GSM and UMTS for voice and SMS services, despite these being incompatible
with LTE. This solution is referred to as Circuit‐Switched Fallback (CSFB) and is
described in this section. Chapter 5 then takes a closer look at the fully IP‐based VoLTE
system that will gradually take over from CSFB in the coming years.
4.13.1 SMS over SGs
One of the most popular services besides voice telephony in wireless networks is SMS.
In GSM, SMS uses the signaling channels of the circuit‐switched side of the network. In
addition, SMS is important for delivering information on international roaming prices
and bill shock‐prevention warning messages to customers. To transport SMS messages
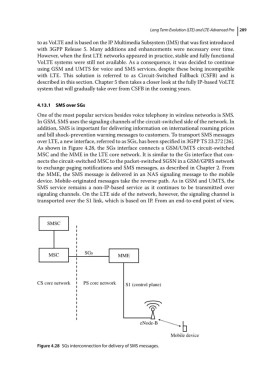
over LTE, a new interface, referred to as SGs, has been specified in 3GPP TS 23.272 [26].
As shown in Figure 4.28, the SGs interface connects a GSM/UMTS circuit‐switched
MSC and the MME in the LTE core network. It is similar to the Gs interface that con-
nects the circuit‐switched MSC to the packet‐switched SGSN in a GSM/GPRS network
to exchange paging notifications and SMS messages, as described in Chapter 2. From
the MME, the SMS message is delivered in an NAS signaling message to the mobile
device. Mobile‐originated messages take the reverse path. As in GSM and UMTS, the
SMS service remains a non‐IP‐based service as it continues to be transmitted over
signaling channels. On the LTE side of the network, however, the signaling channel is
transported over the S1 link, which is based on IP. From an end‐to‐end point of view,
SMSC
MSC SGs MME
CS core network PS core network S1 (control plane)
eNode-B
Mobile device
Figure 4.28 SGs interconnection for delivery of SMS messages.