Page 335 - From GMS to LTE
P. 335
Long Term Evolution (LTE) and LTE-Advanced Pro 321
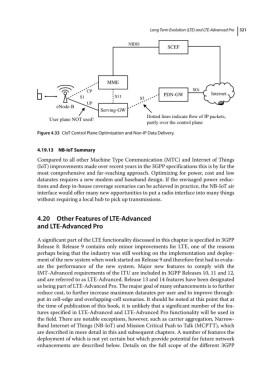
NIDD
SCEF
MME
CP SGi Internet
S1 S11 S5 PDN-GW
UP
eNode-B
Serving-GW
Dotted lines indicate ow of IP packets,
User plane NOT used!
partly over the control plane
Figure 4.33 CIoT Control Plane Optimization and Non‐IP Data Delivery.
4.19.13 NB‐IoT Summary
Compared to all other Machine Type Communication (MTC) and Internet of Things
(IoT) improvements made over recent years in the 3GPP specifications this is by far the
most comprehensive and far‐reaching approach. Optimizing for power, cost and low
datarates requires a new modem and baseband design. If the envisaged power reduc-
tions and deep in‐house coverage scenarios can be achieved in practice, the NB‐IoT air
interface would offer many new opportunities to put a radio interface into many things
without requiring a local hub to pick up transmissions.
4.20 Other Features of LTE‐Advanced
and LTE‐Advanced Pro
A significant part of the LTE functionality discussed in this chapter is specified in 3GPP
Release 8. Release 9 contains only minor improvements for LTE, one of the reasons
perhaps being that the industry was still working on the implementation and deploy-
ment of the new system when work started on Release 9 and therefore first had to evalu-
ate the performance of the new system. Major new features to comply with the
IMT‐Advanced requirements of the ITU are included in 3GPP Releases 10, 11 and 12,
and are referred to as LTE‐Advanced. Release 13 and 14 features have been designated
as being part of LTE‐Advanced Pro. The major goal of many enhancements is to further
reduce cost, to further increase maximum datarates per user and to improve through-
put in cell‐edge and overlapping‐cell scenarios. It should be noted at this point that at
the time of publication of this book, it is unlikely that a significant number of the fea-
tures specified in LTE‐Advanced and LTE‐Advanced Pro functionality will be used in
the field. There are notable exceptions, however, such as carrier aggregation, Narrow‐
Band Internet of Things (NB‐IoT) and Mission Critical Push to Talk (MCPTT), which
are described in more detail in this and subsequent chapters. A number of features the
deployment of which is not yet certain but which provide potential for future network
enhancements are described below. Details on the full scope of the different 3GPP