Page 381 - From GMS to LTE
P. 381
VoLTE, VoWifi and Mission Critical Communication 367
5.4.1 Option 1: VoLTE Local Breakout
The first option standardized for VoLTE roaming in 3GPP Release 11 [22] is referred to
as ‘local breakout’ as it was designed around a similar local handling of VoLTE voice calls
as is used for circuit‐switched calls during roaming, as described above. When a VoLTE‐
roaming‐capable device connects to a visited LTE network abroad and the device recog-
nizes that the network supports the VoLTE Local Breakout mechanism it establishes a
default bearer for IMS signaling. The network recognizes that connectivity for this bearer
shall not be tunneled back to a P‐GW in the home network. Instead the bearer is estab-
lished to a P‐GW in the visited network. The mobile device thus has access to a P‐CSCF
in the visited network, which is important for establishing a dedicated bearer with sepa-
rate quality‐of‐service parameters for VoLTE voice packets. The P‐CSCF recognizes that
it has been contacted by a VoLTE roamer and forwards the SIP Register message to the
I/S‐CSCF in the user’s home network. In addition to the standard IMS SIP registration
process a Transit and Routing Function (TRF) is included in the SIP message routing
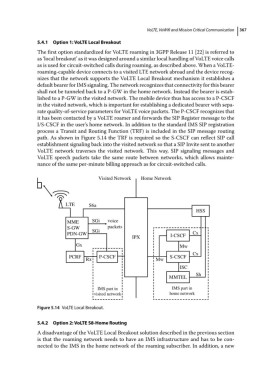
path. As shown in Figure 5.14 the TRF is required so the S‐CSCF can reflect SIP call
establishment signaling back into the visited network so that a SIP Invite sent to another
VoLTE network traverses the visited network. This way, SIP signaling messages and
VoLTE speech packets take the same route between networks, which allows mainte-
nance of the same per‐minute billing approach as for circuit‐switched calls.
Visited Network Home Network
LTE S6a
HSS
MME SGi voice
S-GW packets
PDN-GW SGi I-CSCF Cx
IPX
Gx Mw
Cx
PCRF P-CSCF S-CSCF
Rx Mw
ISC
Sh
MMTEL
IMS part in IMS part in
visited network home network
Figure 5.14 VoLTE Local Breakout.
5.4.2 Option 2: VoLTE S8‐Home Routing
A disadvantage of the VoLTE Local Breakout solution described in the previous section
is that the roaming network needs to have an IMS infrastructure and has to be con-
nected to the IMS in the home network of the roaming subscriber. In addition, a new