Page 412 - From GMS to LTE
P. 412
398 From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G
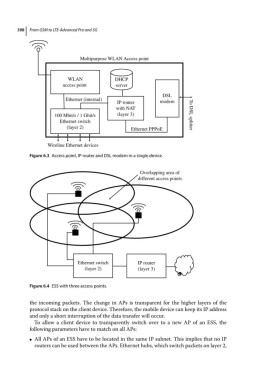
Multipurpose WLAN Access point
WLAN DHCP
access point server
DSL
Ethernet (internal)
IP router modem
with NAT
100 Mbit/s / 1 Gbit/s (layer 3) To DSL splitter
Ethernet switch
(layer 2) Ethernet PPPoE
Wireline Ethernet devices
Figure 6.3 Access point, IP router and DSL modem in a single device.
Overlapping area of
different access points
Ethernet switch IP router
(layer 2) (layer 3)
Figure 6.4 ESS with three access points.
the incoming packets. The change in APs is transparent for the higher layers of the
protocol stack on the client device. Therefore, the mobile device can keep its IP address
and only a short interruption of the data transfer will occur.
To allow a client device to transparently switch over to a new AP of an ESS, the
following parameters have to match on all APs:
All APs of an ESS have to be located in the same IP subnet. This implies that no IP
●
routers can be used between the APs. Ethernet hubs, which switch packets on layer 2,