Page 453 - Handbook of Modern Telecommunications
P. 453
3-244 CRC Handbook of Modern Telecommunications, Second Edition
The traditional answer to the functional view, what should an OSS do, is to either answer with the
TMN pyramid or with FCAPS (Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, and Security man-
agement). The TMN pyramid comes from the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) “TMN
Logical Layered Architecture within the TMN Functional Architecture” [M3010]. This hierarchy is
usually drawn as a pyramid (but does not appear as a pyramid in M.3010). At the base is the element
management layer, followed by the network management layer, the service management layer, with the
business management layer at the top.
While the TMN pyramid can provide valuable insight into functional segmentation, it does not really
say that much about what needs to be accomplished.
The ITU also defines the concept of five functional management areas. These are introduced in M.3010
and elaborated in M.3400 [M3400]. The five areas are usually referred to as FCAPS. While FCAPS does
address some aspects of the “what” question, it addresses functionality from a technical perspective.
First we need to understand the processes that the OSS needs to support and implement. Then we can
look at the technical functionality needed to support the business processes.
3.10.4.1 Service Lifecycles
The approach we take to looking at what an OSS should do is to start by understanding the business
processes that need to be supported. One way of doing this would be to use the eTOM standard as the
base to define the functional view. While eTOM does provide a comprehensive process model for tele-
com companies, what we want to understand is the dynamic view of how the processes work together to
accomplish the business goals.
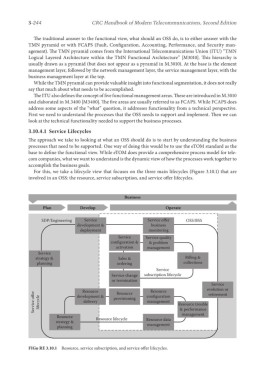
For this, we take a lifecycle view that focuses on the three main lifecycles (Figure 3.10.1) that are
involved in an OSS: the resource, service subscription, and service offer lifecycles.
Business
Plan Develop Operate
SDP/Engineering Service Service offer OSS/BSS
development & business
deployment monitoring
Service Service quality
configuration & & problem
activation management
Service
strategy & Sales & Billing &
planning ordering collections
Service
Service change subscription lifecycle
or termination
Service
Resource Resource configuration evolution or
Resource
Service offer lifecycle delivery provisioning management Resource trouble
retirement
development &
& performance
Resource Resource lifecycle management
strategy & Resource data
planning management
FIGu RE 3.10.1 Resource, service subscription, and service offer lifecycles.