Page 301 - Foundations of Marketing
P. 301
268 Part 4 | Product and Price Decisions
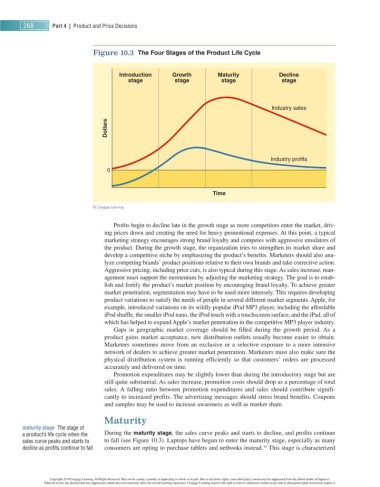
Figure 10.3 The Four Stages of the Product Life Cycle
Introduction Growth Maturity Decline
stage stage stage stage
Industry sales
Dollars
Industry profits
0
Time
© Cengage Learning
Profi ts begin to decline late in the growth stage as more competitors enter the market, driv-
ing prices down and creating the need for heavy promotional expenses. At this point, a typical
marketing strategy encourages strong brand loyalty and competes with aggressive emulators of
the product. During the growth stage, the organization tries to strengthen its market share and
develop a competitive niche by emphasizing the product’s benefi ts. Marketers should also ana-
lyze competing brands’ product positions relative to their own brands and take corrective action.
Aggressive pricing, including price cuts, is also typical during this stage. As sales increase, man-
agement must support the momentum by adjusting the marketing strategy. The goal is to estab-
lish and fortify the product’s market position by encouraging brand loyalty. To achieve greater
market penetration, segmentation may have to be used more intensely. This requires developing
product variations to satisfy the needs of people in several different market segments. Apple, for
example, introduced variations on its wildly popular iPod MP3 player, including the affordable
iPod shuffl e, the smaller iPod nano, the iPod touch with a touchscreen surface, and the iPad, all of
which has helped to expand Apple’s market penetration in the competitive MP3 player industry.
Gaps in geographic market coverage should be filled during the growth period. As a
product gains market acceptance, new distribution outlets usually become easier to obtain.
Marketers sometimes move from an exclusive or a selective exposure to a more intensive
network of dealers to achieve greater market penetration. Marketers must also make sure the
physical distribution system is running efficiently so that customers’ orders are processed
accurately and delivered on time.
Promotion expenditures may be slightly lower than during the introductory stage but are
still quite substantial. As sales increase, promotion costs should drop as a percentage of total
sales. A falling ratio between promotion expenditures and sales should contribute signifi-
cantly to increased profits. The advertising messages should stress brand benefits. Coupons
and samples may be used to increase awareness as well as market share.
Maturity
maturity stage The stage of
a product’s life cycle when the During the maturity stage , the sales curve peaks and starts to decline, and profits continue
sales curve peaks and starts to to fall (see Figure 10.3 ). Laptops have begun to enter the maturity stage, especially as many
14
decline as profits continue to fall consumers are opting to purchase tablets and netbooks instead. This stage is characterized
Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.