Page 401 - Foundations of Marketing
P. 401
368 Part 5 | Distribution Decisions
Channel D, wherein goods pass from producer, to agents, to wholesalers, to retailers, and
finally to consumers, is used frequently for products intended for mass distribution, such as
processed foods. For example, to place its Wheat Thins crackers in specific retail outlets,
supply-chain managers at Nabisco may hire an agent (or a food broker) to sell the crackers to
wholesalers. Wholesalers then sell the Wheat Thins to supermarkets, vending-machine opera-
tors, and convenience stores.
A long channel may actually be the most efficient distribution channel for some goods.
When several channel intermediaries perform specialized functions at which they are experts,
costs may be lower than when one channel member tries to perform them all. Efficiencies arise
when firms that specialize in certain elements of producing a product or moving it through the
channel are more effective at performing specialized tasks than the manufacturer. This results
in added value to customers.
Channels for Business Products
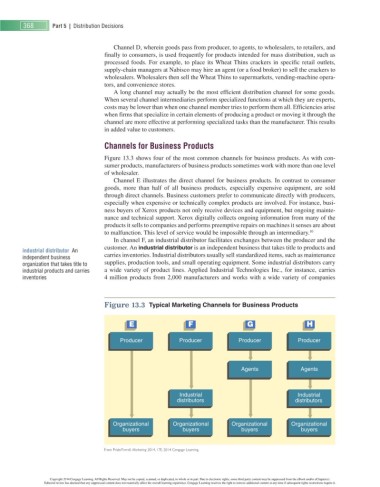
Figure 13.3 shows four of the most common channels for business products. As with con-
sumer products, manufacturers of business products sometimes work with more than one level
of wholesaler.
Channel E illustrates the direct channel for business products. In contrast to consumer
goods, more than half of all business products, especially expensive equipment, are sold
through direct channels. Business customers prefer to communicate directly with producers,
especially when expensive or technically complex products are involved. For instance, busi-
ness buyers of Xerox products not only receive devices and equipment, but ongoing mainte-
nance and technical support. Xerox digitally collects ongoing information from many of the
products it sells to companies and performs preemptive repairs on machines it senses are about
10
to malfunction. This level of service would be impossible through an intermediary.
In channel F, an industrial distributor facilitates exchanges between the producer and the
customer. An industrial distributor is an independent business that takes title to products and
industrial distributor An
independent business carries inventories. Industrial distributors usually sell standardized items, such as maintenance
organization that takes title to supplies, production tools, and small operating equipment. Some industrial distributors carry
industrial products and carries a wide variety of product lines. Applied Industrial Technologies Inc., for instance, carries
inventories 4 million products from 2,000 manufacturers and works with a wide variety of companies
Figure 13.3 Typical Marketing Channels for Business Products
E F G H
Producer Producer Producer Producer
Agents Agents
Industrial Industrial
distributors distributors
Organizational Organizational Organizational Organizational
buyers buyers buyers buyers
From Pride/Ferrell, Marketing 2014, 17E. 2014 Cengage Learning.
Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.