Page 51 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 51
fuel reactions in the 2 Calvin cycle. In these reactions, carbon
atoms from carbon dioxide are linked together to manufacture
sugars. Photosynthesis is a complex process, but the overall
reaction can be summarized with the following equation:
6CO 1 12H O 1 the sun’s S C H O 1 6O 1 6H O
Light energy 2 2 6 12 6 2 2
energy (sugar)
The number preceding each molecular formula indi-
Chloroplast cates how many of those molecules are involved in the reac-
tion. Note that the sums of the numbers on each side of the
1 Light reactions H O O 2 equation for each element are equal; that is, there are 6 C,
2
24 H, and 24 O atoms on each side. This illustrates how
ATP ADP chemical equations are balanced, with each atom recycled
NADP + and matter conserved. No atoms are lost; they are simply
NADPH Inorganic rearranged among molecules. Note also that water appears
phosphate on both sides of the equation. The reason is that for every
12 water molecules that are input and split in the process,
6 water molecules are newly created. We can streamline the
photosynthesis equation by showing only the net loss of 6
water molecules:
2 Calvin cycle CO 2 Sugars
6CO 1 6H O 1 the sun’s energy S C H O 1 6O
2 2 6 12 6 2
(sugar)
Thus, in photosynthesis, water, carbon dioxide, and
light energy from the sun are transformed to produce sugar
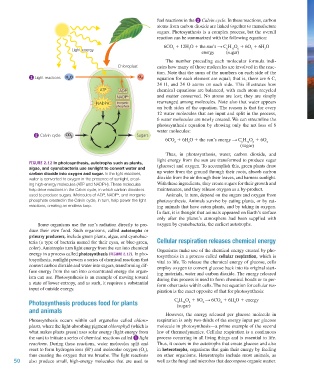
Figure 2.12 In photosynthesis, autotrophs such as plants,
algae, and cyanobacteria use sunlight to convert water and (glucose) and oxygen. To accomplish this, green plants draw
carbon dioxide into oxygen and sugar. In the light reactions, up water from the ground through their roots, absorb carbon
water is converted to oxygen in the presence of sunlight, creat- dioxide from the air through their leaves, and harness sunlight.
ing high-energy molecules (ATP and NADPH). These molecules With these ingredients, they create sugars for their growth and
help drive reactions in the Calvin cycle, in which carbon dioxide is maintenance, and they release oxygen as a by-product.
used to produce sugars. Molecules of ADP, NADP , and inorganic Animals, in turn, depend on the sugars and oxygen from
+
phosphate created in the Calvin cycle, in turn, help power the light photosynthesis. Animals survive by eating plants, or by eat-
reactions, creating an endless loop. ing animals that have eaten plants, and by taking in oxygen.
In fact, it is thought that animals appeared on Earth’s surface
only after the planet’s atmosphere had been supplied with
Some organisms use the sun’s radiation directly to pro- oxygen by cyanobacteria, the earliest autotrophs.
duce their own food. Such organisms, called autotrophs or
primary producers, include green plants, algae, and cyanobac-
teria (a type of bacteria named for their cyan, or blue-green, Cellular respiration releases chemical energy
color). Autotrophs turn light energy from the sun into chemical Organisms make use of the chemical energy created by pho-
energy in a process called photosynthesis (Figure 2.12). In pho- tosynthesis in a process called cellular respiration, which is
tosynthesis, sunlight powers a series of chemical reactions that vital to life. To release the chemical energy of glucose, cells
convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars, transforming dif- employ oxygen to convert glucose back into its original start-
fuse energy from the sun into concentrated energy the organ- ing materials, water and carbon dioxide. The energy released
ism can use. Photosynthesis is an example of moving toward during this process is used to form chemical bonds or to per-
a state of lower entropy, and as such, it requires a substantial form other tasks within cells. The net equation for cellular res-
input of outside energy.
piration is the exact opposite of that for photosynthesis:
Photosynthesis produces food for plants C H O 1 6O S 6CO 1 6H O 1 energy
2
12
6
2
2
6
(sugar)
and animals
However, the energy released per glucose molecule in
Photosynthesis occurs within cell organelles called chloro- respiration is only two-thirds of the energy input per glucose
plasts, where the light-absorbing pigment chlorophyll (which is molecule in photosynthesis—a prime example of the second
what makes plants green) uses solar energy (light energy from law of thermodynamics. Cellular respiration is a continuous
the sun) to initiate a series of chemical reactions called 1 light process occurring in all living things and is essential to life.
reactions. During these reactions, water molecules split and Thus, it occurs in the autotrophs that create glucose and also
react to form hydrogen ions (H ) and molecular oxygen (O ), in heterotrophs, organisms that gain their energy by feeding
+
2
thus creating the oxygen that we breathe. The light reactions on other organisms. Heterotrophs include most animals, as
50 also produce small, high-energy molecules that are used to well as the fungi and microbes that decompose organic matter.
M02_WITH7428_05_SE_C02.indd 50 12/12/14 2:53 PM