Page 555 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 555
putting a hold on further approvals until new safety measures Addressing Impacts
could be devised.
In 2011, after weighing economic and environmental con- of Fossil Fuel Use
cerns, the administration issued a five-year plan that opened
access to 75% of technically recoverable offshore oil and gas Our society’s love affair with fossil fuels and the many petro-
reserves while banning drilling offshore from states that did chemical products we develop from them has helped to ease
not want it. Drilling leases were expanded off Alaska and in constraints on travel, lengthen our life spans, and boost our
the Gulf of Mexico, but areas along the East and West Coasts material standard of living beyond what our ancestors could
were not opened to drilling. have dreamed. However, it also causes harm to the environ-
The risks from expansion into Arctic waters were high- ment and human health, and can lead to political and economic
lighted in 2012–2013, when Royal Dutch Shell’s Kulluk instability. Concern over these impacts is a prime reason many
drilling rig ran aground while being towed south from Alaska scientists, environmental advocates, businesspeople, and poli-
during a winter storm. Damage to the rig and examination by cymakers are increasingly looking toward clean and renew-
public officials and the media raised fresh questions as to able sources of energy.
whether Arctic Ocean drilling can be conducted safely.
Fossil fuel emissions pollute air and drive
We are exploiting new fossil fuel sources climate change
As sources of conventional fossil fuels decline and as prices When we burn fossil fuels, we alter fluxes in Earth’s carbon
rise, we will turn increasingly to newer alternatives. These cycle (pp. 139–141). We essentially take carbon that has been
include at least three further sources of fossil fuels that exist in retired into a long-term reservoir underground and release it
large amounts: oil sands, oil shale, and methane hydrate. The into the air. This occurs as carbon from the hydrocarbon mol-
oil sands of Alberta—and those in Venezuela, which likely ecules of fossil fuels unites with oxygen from the atmosphere
hold even more oil—are already significantly increasing the during combustion, producing carbon dioxide (CO ). Carbon
2
amount of oil available to our society. Oil from shale is not yet dioxide is a greenhouse gas (p. 502), and CO released from
2
economical to extract. Gas from methane hydrate is only now fossil fuel combustion warms our planet and drives changes in
becoming technically feasible to extract. global climate (Chapter 18).
The world’s known deposits of oil shale may contain as Because global climate change is beginning to have
much as 3 trillion barrels of oil (more than all the conven- diverse, severe, and widespread ecological and socioeconomic
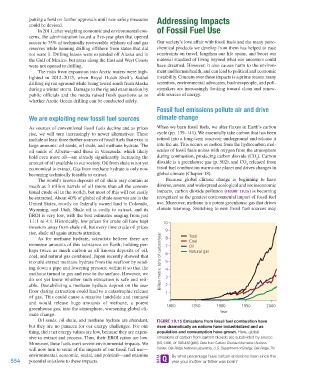
tional crude oil in the world), but most of this will not easily impacts, carbon dioxide pollution (FIGURE 19.15) is becoming
be extracted. About 40% of global oil shale reserves are in the recognized as the greatest environmental impact of fossil fuel
United States, mostly on federally owned land in Colorado, use. Moreover, methane is a potent greenhouse gas that drives
Wyoming, and Utah. Shale oil is costly to extract, and its climate warming. Switching to new fossil fuel sources may
EROI is very low, with the best estimates ranging from just
1.1:1 to 4:1. Historically, low prices for crude oil have kept 10
investors away from shale oil, but every time crude oil prices
rise, shale oil again attracts attention. 9
As for methane hydrate, scientists believe there are 8 Total
immense amounts of this substance on Earth, holding per- 7 Coal
Oil
haps twice as much carbon as all known deposits of oil, Natural gas
coal, and natural gas combined. Japan recently showed that 6
it could extract methane hydrate from the seafloor by send- Billion metric tons of carbon/year 5
ing down a pipe and lowering pressure within it so that the 4
methane turned to gas and rose to the surface. However, we
do not yet know whether such extraction is safe and reli- 3
able. Destabilizing a methane hydrate deposit on the sea- 2
floor during extraction could lead to a catastrophic release 1
of gas. This could cause a massive landslide and tsunami
and would release huge amounts of methane, a potent
greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere, worsening global cli- 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000
mate change. Year
Oil sands, oil shale, and methane hydrate are abundant, FIGURE 19.15 Emissions from fossil fuel combustion have
but they are no panacea for our energy challenges. For one risen dramatically as nations have industrialized and as
thing, their net energy values are low, because they are expen- population and consumption have grown. Here, global
sive to extract and process. Thus, their EROI ratios are low. emissions of carbon from carbon dioxide are subdivided by source
Moreover, these fuels exert severe environmental impacts. We (oil, coal, or natural gas). Data from Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis
will now turn to some of the impacts of our fossil fuel use— Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge, TN.
environmental, economic, social, and political—and examine By what percentage have carbon emissions risen since the
554 potential solutions to these impacts. year your mother or father was born?
M19_WITH7428_05_SE_C19.indd 554 12/12/14 5:23 PM