Page 704 - Basic College Mathematics with Early Integers
P. 704
CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 681
Definitions and Concepts Examples
Section 9.1 Lines and Angles (continued)
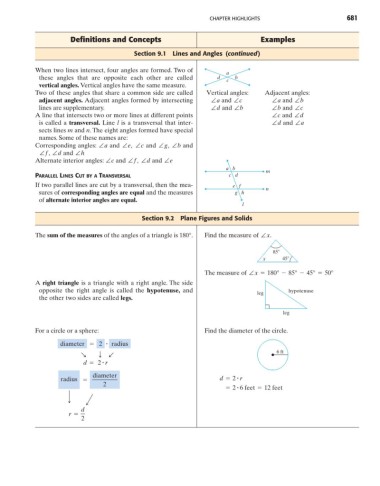
When two lines intersect, four angles are formed. Two of
a
these angles that are opposite each other are called d c b
vertical angles. Vertical angles have the same measure.
Two of these angles that share a common side are called Vertical angles: Adjacent angles:
adjacent angles. Adjacent angles formed by intersecting ∠a and ∠c ∠a and ∠b
lines are supplementary. ∠d and ∠b ∠b and ∠c
A line that intersects two or more lines at different points ∠c and ∠d
is called a transversal. Line l is a transversal that inter- ∠d and ∠a
sects lines m and n. The eight angles formed have special
names. Some of these names are:
Corresponding angles: ∠a and ∠e, ∠c and ∠g, ∠b and
∠f, ∠d and ∠h
Alternate interior angles: ∠c and ∠f, ∠d and ∠e
ab m
PARALLEL LINES CUT BY A TRANSVERSAL cd
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the mea- ef n
sures of corresponding angles are equal and the measures gh
of alternate interior angles are equal.
l
Section 9.2 Plane Figures and Solids
The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180°. Find the measure of ∠x.
85
x 45
The measure of ∠x = 180° - 85° - 45° = 50°
A right triangle is a triangle with a right angle. The side
opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse, and hypotenuse
leg
the other two sides are called legs.
leg
For a circle or a sphere: Find the diameter of the circle.
diameter = 2 # radius
6 ft
R T b
#
d = 2 r
diameter #
radius = d = 2 r
2
#
= 2 6 feet = 12 feet
∂ ∂
d
r =
2