Page 124 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 124
= 5 × 50 − 100 (− 15) + 10 (− 200)
= 250 + 1500 − 2000
= − 250
It can be observed that multiplication of the minor is done alternately as positive and negative
starting from the first row or the first column. Now we will take up a few numerical problems
to calculate branch currents in an electric network.
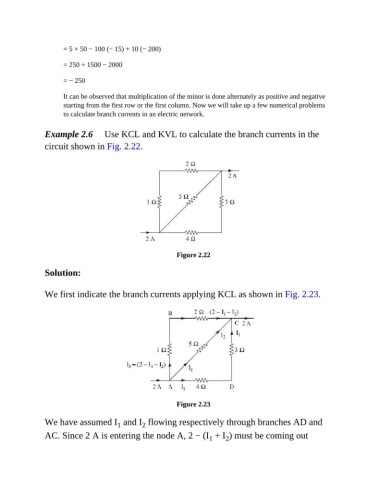
Example 2.6 Use KCL and KVL to calculate the branch currents in the
circuit shown in Fig. 2.22.
Figure 2.22
Solution:
We first indicate the branch currents applying KCL as shown in Fig. 2.23.
Figure 2.23
We have assumed I and I flowing respectively through branches AD and
2
1
AC. Since 2 A is entering the node A, 2 − (I + I ) must be coming out
2
1