Page 533 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 533
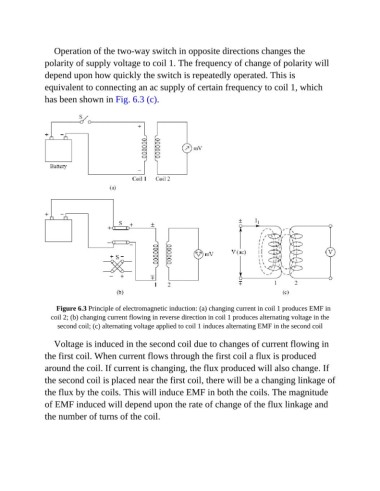
Operation of the two-way switch in opposite directions changes the
polarity of supply voltage to coil 1. The frequency of change of polarity will
depend upon how quickly the switch is repeatedly operated. This is
equivalent to connecting an ac supply of certain frequency to coil 1, which
has been shown in Fig. 6.3 (c).
Figure 6.3 Principle of electromagnetic induction: (a) changing current in coil 1 produces EMF in
coil 2; (b) changing current flowing in reverse direction in coil 1 produces alternating voltage in the
second coil; (c) alternating voltage applied to coil 1 induces alternating EMF in the second coil
Voltage is induced in the second coil due to changes of current flowing in
the first coil. When current flows through the first coil a flux is produced
around the coil. If current is changing, the flux produced will also change. If
the second coil is placed near the first coil, there will be a changing linkage of
the flux by the coils. This will induce EMF in both the coils. The magnitude
of EMF induced will depend upon the rate of change of the flux linkage and
the number of turns of the coil.