Page 242 - Using MIS
P. 242
210 Chapter 6 The Cloud
in Q2 and Q3. Before we define and explain those terms, however, let’s consider factors that
make the cloud the future.
Why Is the Cloud Preferred to In-House Hosting?
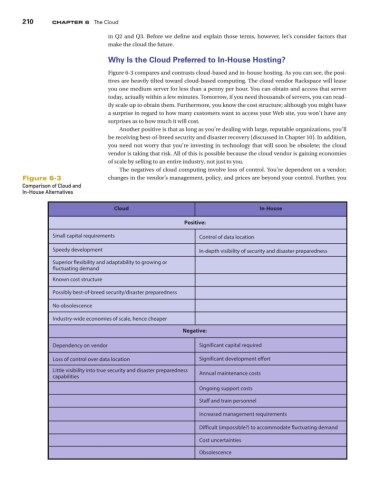
Figure 6-3 compares and contrasts cloud-based and in-house hosting. As you can see, the posi-
tives are heavily tilted toward cloud-based computing. The cloud vendor Rackspace will lease
you one medium server for less than a penny per hour. You can obtain and access that server
today, actually within a few minutes. Tomorrow, if you need thousands of servers, you can read-
ily scale up to obtain them. Furthermore, you know the cost structure; although you might have
a surprise in regard to how many customers want to access your Web site, you won’t have any
surprises as to how much it will cost.
Another positive is that as long as you’re dealing with large, reputable organizations, you’ll
be receiving best-of-breed security and disaster recovery (discussed in Chapter 10). In addition,
you need not worry that you’re investing in technology that will soon be obsolete; the cloud
vendor is taking that risk. All of this is possible because the cloud vendor is gaining economies
of scale by selling to an entire industry, not just to you.
The negatives of cloud computing involve loss of control. You’re dependent on a vendor;
Figure 6-3 changes in the vendor’s management, policy, and prices are beyond your control. Further, you
Comparison of Cloud and
In-House Alternatives
Cloud In-House
Positive:
Small capital requirements Control of data location
Speedy development In-depth visibility of security and disaster preparedness
Superior flexibility and adaptability to growing or
fluctuating demand
Known cost structure
Possibly best-of-breed security/disaster preparedness
No obsolescence
Industry-wide economies of scale, hence cheaper
Negative:
Dependency on vendor Significant capital required
Loss of control over data location Significant development eort
Little visibility into true security and disaster preparedness Annual maintenance costs
capabilities
Ongoing support costs
Sta and train personnel
Increased management requirements
Difficult (impossible?) to accommodate uctuating demand
Cost uncertainties
Obsolescence