Page 247 - Using MIS
P. 247
Q2 What Network Technology Supports the Cloud? 215
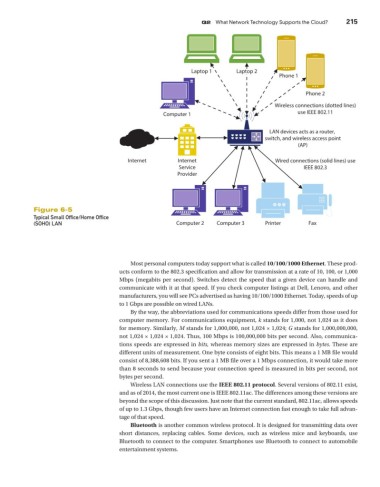
Laptop 1 Laptop 2
Phone 1
Phone 2
Wireless connections (dotted lines)
Computer 1 use IEEE 802.11
LAN devices acts as a router,
switch, and wireless access point
(AP)
Internet Internet Wired connections (solid lines) use
Service IEEE 802.3
Provider
Figure 6-5
Typical Small Office/Home Office
(SOHO) LAN Computer 2 Computer 3 Printer Fax
Most personal computers today support what is called 10/100/1000 Ethernet. These prod-
ucts conform to the 802.3 specification and allow for transmission at a rate of 10, 100, or 1,000
Mbps (megabits per second). Switches detect the speed that a given device can handle and
communicate with it at that speed. If you check computer listings at Dell, Lenovo, and other
manufacturers, you will see PCs advertised as having 10/100/1000 Ethernet. Today, speeds of up
to 1 Gbps are possible on wired LANs.
By the way, the abbreviations used for communications speeds differ from those used for
computer memory. For communications equipment, k stands for 1,000, not 1,024 as it does
for memory. Similarly, M stands for 1,000,000, not 1,024 × 1,024; G stands for 1,000,000,000,
not 1,024 × 1,024 × 1,024. Thus, 100 Mbps is 100,000,000 bits per second. Also, communica-
tions speeds are expressed in bits, whereas memory sizes are expressed in bytes. These are
different units of measurement. One byte consists of eight bits. This means a 1 MB file would
consist of 8,388,608 bits. If you sent a 1 MB file over a 1 Mbps connection, it would take more
than 8 seconds to send because your connection speed is measured in bits per second, not
bytes per second.
Wireless LAN connections use the IEEE 802.11 protocol. Several versions of 802.11 exist,
and as of 2014, the most current one is IEEE 802.11ac. The differences among these versions are
beyond the scope of this discussion. Just note that the current standard, 802.11ac, allows speeds
of up to 1.3 Gbps, though few users have an Internet connection fast enough to take full advan-
tage of that speed.
Bluetooth is another common wireless protocol. It is designed for transmitting data over
short distances, replacing cables. Some devices, such as wireless mice and keyboards, use
Bluetooth to connect to the computer. Smartphones use Bluetooth to connect to automobile
entertainment systems.