Page 328 - Using MIS
P. 328
296 Chapter 8 Social Media Information Systems
community. The key difference of SM communities is that they are formed based on mutual
interests and transcend familial, geographic, and organizational boundaries.
Because of this transcendence, most people belong to several, or even many, different user
communities. Google+ recognized this fact when it created user circles that enable users to allo-
cate their connections (people, using Google+ terminology) to one or more community groups.
Facebook and other SM application providers are adapting in similar ways.
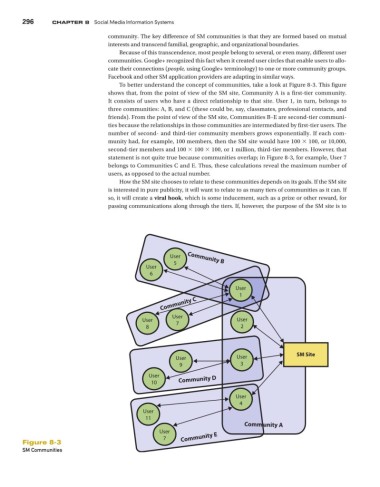
To better understand the concept of communities, take a look at Figure 8-3. This figure
shows that, from the point of view of the SM site, Community A is a first-tier community.
It consists of users who have a direct relationship to that site. User 1, in turn, belongs to
three communities: A, B, and C (these could be, say, classmates, professional contacts, and
friends). From the point of view of the SM site, Communities B–E are second-tier communi-
ties because the relationships in those communities are intermediated by first-tier users. The
number of second- and third-tier community members grows exponentially. If each com-
munity had, for example, 100 members, then the SM site would have 100 × 100, or 10,000,
second-tier members and 100 × 100 × 100, or 1 million, third-tier members. However, that
statement is not quite true because communities overlap; in Figure 8-3, for example, User 7
belongs to Communities C and E. Thus, these calculations reveal the maximum number of
users, as opposed to the actual number.
How the SM site chooses to relate to these communities depends on its goals. If the SM site
is interested in pure publicity, it will want to relate to as many tiers of communities as it can. If
so, it will create a viral hook, which is some inducement, such as a prize or other reward, for
passing communications along through the tiers. If, however, the purpose of the SM site is to
User Community B
5
User
6
User
1
Community C
User
User 7 User
8 2
User User SM Site
9 3
User
10 Community D
User
4
User
11
Community A
User
7 Community E
Figure 8-3
SM Communities