Page 508 - Using MIS
P. 508
476 Chapter 12 Information Systems Development
As the name implies, with phased installation the new system/business processes are
installed in phases across the organization(s). Once a given piece works, then the organization
installs and tests another piece of the system, until the entire system has been installed. Some
systems are so tightly integrated that they cannot be installed in phased pieces. Such systems
must be installed using one of the other techniques.
With parallel installation, the new system/business processes run parallel with the old one
until the new system is tested and fully operational. Parallel installation is expensive because
the organization incurs the costs of running both the existing and the new system/business pro-
cesses. Users must work double-time, if you will, to run both systems. Then considerable work is
needed to reconcile the results of the new with the old.
The final style of conversion is plunge installation (sometimes called direct installation).
With it, the organization shuts off the old system/business processes and starts the new one. If
the new system/business processes fail, the organization is in trouble: Nothing can be done until
either the new system/business processes are fixed or the old ones are reinstalled. Because of the
risk, organizations should avoid this conversion style if possible. The one exception is if the new
system is providing a new capability that will not disrupt the operation of the organization if it fails.
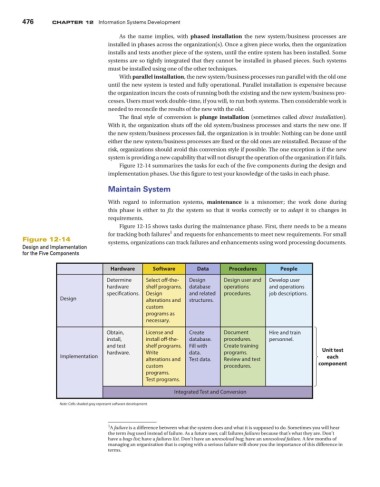
Figure 12-14 summarizes the tasks for each of the five components during the design and
implementation phases. Use this figure to test your knowledge of the tasks in each phase.
Maintain System
With regard to information systems, maintenance is a misnomer; the work done during
this phase is either to fix the system so that it works correctly or to adapt it to changes in
requirements.
Figure 12-15 shows tasks during the maintenance phase. First, there needs to be a means
1
for tracking both failures and requests for enhancements to meet new requirements. For small
Figure 12-14 systems, organizations can track failures and enhancements using word processing documents.
Design and Implementation
for the Five Components
Hardware Software Data Procedures People
Determine Select o -the- Design Design user and Develop user
hardware shelf programs. database operations and operations
specications. Design and related procedures. job descriptions.
Design alterations and structures.
custom
programs as
necessary.
Obtain, License and Create Document Hire and train
install, install o -the- database. procedures. personnel.
and test shelf programs. Fill with Create training
hardware. Write data. programs. Unit test
Implementation alterations and Test data. Review and test each
custom procedures. component
programs.
Test programs.
Integrated Test and Conversion
Note: Cells shaded gray represent software development.
1 A failure is a difference between what the system does and what it is supposed to do. Sometimes you will hear
the term bug used instead of failure. As a future user, call failures failures because that’s what they are. Don’t
have a bugs list; have a failures list. Don’t have an unresolved bug; have an unresolved failure. A few months of
managing an organization that is coping with a serious failure will show you the importance of this difference in
terms.