Page 10 - Instrumentation and Measurement
P. 10
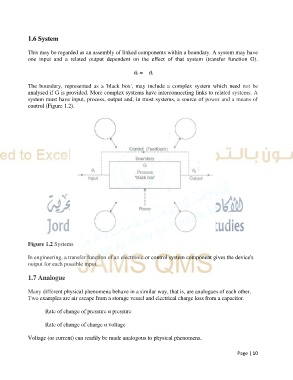
1.6 System
This may be regarded as an assembly of linked components within a boundary. A system may have
one input and a related output dependent on the effect of that system (transfer function G).
o = Gi
The boundary, represented as a 'black box', may include a complex system which need not be
analysed if G is provided. More complex systems have interconnecting links to related systems. A
system must have input, process, output and, in most systems, a source of power and a means of
control (Figure 1.2).
Figure 1.2 Systems
In engineering, a transfer function of an electronic or control system component gives the device's
output for each possible input.
1.7 Analogue
Many different physical phenomena behave in a similar way, that is, are analogues of each other.
Two examples are air escape from a storage vessel and electrical charge loss from a capacitor.
Rate of change of pressure α pressure
Rate of change of charge α voltage
Voltage (or current) can readily be made analogous to physical phenomena.
Page | 10