Page 36 - Instrumentation and Measurement
P. 36
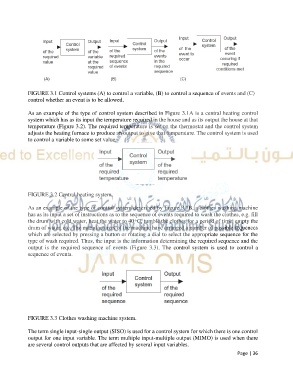
FIGURE 3.1 Control systems (A) to control a variable, (B) to control a sequence of events and (C)
control whether an event is to be allowed.
As an example of the type of control system described in Figure 3.1A is a central heating control
system which has as its input the temperature required in the house and as its output the house at that
temperature (Figure 3.2). The required temperature is set on the thermostat and the control system
adjusts the heating furnace to produce an output to give that temperature. The control system is used
to control a variable to some set value.
FIGURE 3.2 Central heating system.
As an example of the type of control system described by Figure 3.1B, a clothes washing machine
has as its input a set of instructions as to the sequence of events required to wash the clothes, e.g. fill
the drum with cold water, heat the water to 40 ͦ C, tumble the clothes for a period of time, empty the
drum of water, etc. The manufacturers of the machine have arranged a number of possible sequences
which are selected by pressing a button or rotating a dial to select the appropriate sequence for the
type of wash required. Thus, the input is the information determining the required sequence and the
output is the required sequence of events (Figure 3.3). The control system is used to control a
sequence of events.
FIGURE 3.3 Clothes washing machine system.
The term single input-single output (SISO) is used for a control system for which there is one control
output for one input variable. The term multiple input-multiple output (MIMO) is used when there
are several control outputs that are affected by several input variables.
Page | 36