Page 11 - FINAL CFA I SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 12
P. 11
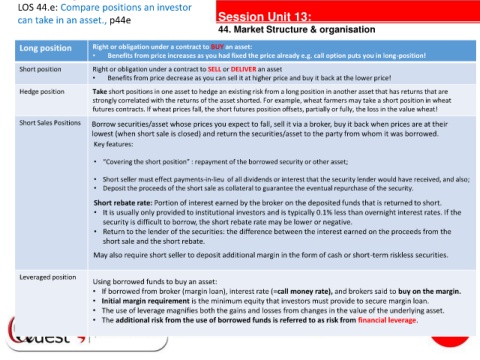
LOS 44.e: Compare positions an investor
can take in an asset., p44e Session Unit 13:
44. Market Structure & organisation
Long position Right or obligation under a contract to BUY an asset:
• Benefits from price increases as you had fixed the price already e.g. call option puts you in long-position!
Short position Right or obligation under a contract to SELL or DELIVER an asset
• Benefits from price decrease as you can sell it at higher price and buy it back at the lower price!
Hedge position Take short positions in one asset to hedge an existing risk from a long position in another asset that has returns that are
strongly correlated with the returns of the asset shorted. For example, wheat farmers may take a short position in wheat
futures contracts. If wheat prices fall, the short futures position offsets, partially or fully, the loss in the value wheat!
Short Sales Positions Borrow securities/asset whose prices you expect to fall, sell it via a broker, buy it back when prices are at their
lowest (when short sale is closed) and return the securities/asset to the party from whom it was borrowed.
Key features:
tanties
• “Covering the short position” : repayment of the borrowed security or other asset;
• Short seller must effect payments-in-lieu of all dividends or interest that the security lender would have received, and also;
• Deposit the proceeds of the short sale as collateral to guarantee the eventual repurchase of the security.
Short rebate rate: Portion of interest earned by the broker on the deposited funds that is returned to short.
• It is usually only provided to institutional investors and is typically 0.1% less than overnight interest rates. If the
security is difficult to borrow, the short rebate rate may be lower or negative.
• Return to the lender of the securities: the difference between the interest earned on the proceeds from the
short sale and the short rebate.
May also require short seller to deposit additional margin in the form of cash or short-term riskless securities.
Leveraged position
Using borrowed funds to buy an asset:
• If borrowed from broker (margin loan), interest rate (=call money rate), and brokers said to buy on the margin.
• Initial margin requirement is the minimum equity that investors must provide to secure margin loan.
• The use of leverage magnifies both the gains and losses from changes in the value of the underlying asset.
• The additional risk from the use of borrowed funds is referred to as risk from financial leverage.