Page 9 - FINAL CFA I SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 12
P. 9
LOS 44.d: Describe types of financial
intermediaries and services that they provide., Session Unit 13:
44. Market Structure & organisation
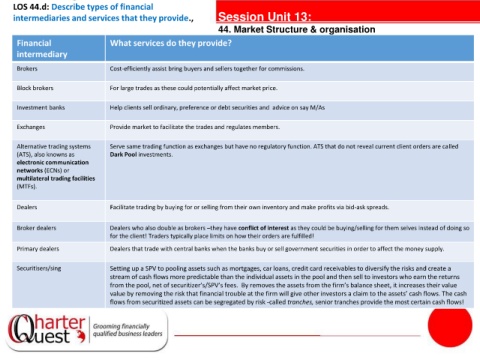
Financial What services do they provide?
intermediary
Brokers Cost-efficiently assist bring buyers and sellers together for commissions.
Block brokers For large trades as these could potentially affect market price.
Investment banks Help clients sell ordinary, preference or debt securities and advice on say M/As
Exchanges Provide market to facilitate the trades and regulates members.
Alternative trading systems Serve same trading function as exchanges but have no regulatory function. ATS that do not reveal current client orders are called
(ATS), also knowns as Dark Pool investments. tanties
electronic communication
networks (ECNs) or
multilateral trading facilities
(MTFs).
Dealers Facilitate trading by buying for or selling from their own inventory and make profits via bid-ask spreads.
Broker dealers Dealers who also double as brokers –they have conflict of interest as they could be buying/selling for them selves instead of doing so
for the client! Traders typically place limits on how their orders are fulfilled!
Primary dealers Dealers that trade with central banks when the banks buy or sell government securities in order to affect the money supply.
Securitisers/sing Setting up a SPV to pooling assets such as mortgages, car loans, credit card receivables to diversify the risks and create a
stream of cash flows more predictable than the individual assets in the pool and then sell to investors who earn the returns
from the pool, net of securitizer’s/SPV’s fees. By removes the assets from the firm’s balance sheet, it increases their value
value by removing the risk that financial trouble at the firm will give other investors a claim to the assets’ cash flows. The cash
flows from securitized assets can be segregated by risk -called tranches, senior tranches provide the most certain cash flows!