Page 208 - Microsoft Word - 00 CIMA F1 Prelims STUDENT 2018.docx
P. 208
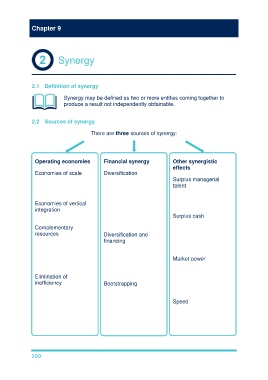
Chapter 9
Synergy
2.1 Definition of synergy
Synergy may be defined as two or more entities coming together to
produce a result not independently obtainable.
2.2 Sources of synergy
There are three sources of synergy:
Operating economies Financial synergy Other synergistic
effects
Economies of scale – Diversification – reduces
can occur in the risk, so even if the Surplus managerial
production, marketing or earnings stay the same talent – the acquisition of
finance areas. (i.e. no operating inefficient companies is
economies are a good way to utilise
Economies of vertical obtained), there could skilled managers.
integration – 'cutting out still be an increase in
the middle man'. value of the company Surplus cash –
due to the lower risk. acquisition uses surplus
Complementary cash if increased
resources – e.g. Diversification and dividends are not
combining an R&D financing – the variability considered to be
company with a of operating cash flows appropriate.
company strong in may be reduced, which
marketing could lead to is more attractive to Market power –
gains. creditors so could lead horizontal combinations
to cheaper financing. may give monopoly
Elimination of power that can increase
inefficiency – If the victim Bootstrapping – profitability (but beware
company is badly companies with high P/E competition authorities).
managed. ratios are in a good
position to acquire other Speed – acquisition is
companies as they can usually much faster than
impose their high P/E organic growth.
ratio on the victim firm
and increase its value.
200