Page 35 - F2 - MA Integrated Workbook STUDENT 2018-19
P. 35
Sources of data
Sampling
5.1 Sampling methods
Sampling is appropriate when we can select units (e.g. people, organisations) from a
population of interest; so that by studying the sample, we may fairly generalise our
results back to the whole population.
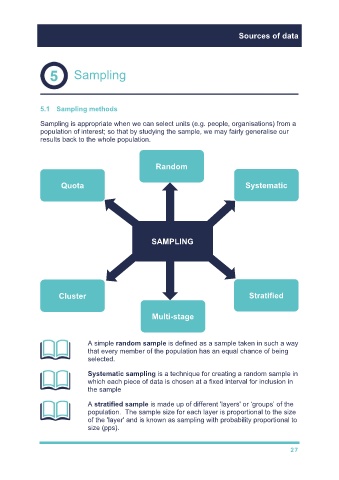
Random
Quota Systematic
SAMPLING
Cluster Stratified
Multi-stage
A simple random sample is defined as a sample taken in such a way
that every member of the population has an equal chance of being
selected.
Systematic sampling is a technique for creating a random sample in
which each piece of data is chosen at a fixed interval for inclusion in
the sample
A stratified sample is made up of different 'layers' or ‘groups’ of the
population. The sample size for each layer is proportional to the size
of the 'layer' and is known as sampling with probability proportional to
size (pps).
27